Divergent cardio-ventilatory and locomotor effects of centrally and peripherally administered urotensin II and urotensin II-related peptides in trout
- PMID: 25954149
- PMCID: PMC4406059
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00142
Divergent cardio-ventilatory and locomotor effects of centrally and peripherally administered urotensin II and urotensin II-related peptides in trout
Abstract
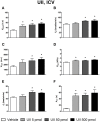
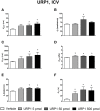
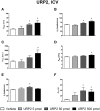
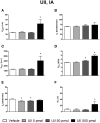
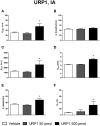
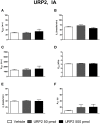
The urotensin II (UII) gene family consists of four paralogous genes called UII, UII-related peptide (URP), URP1 and URP2. UII and URP peptides exhibit the same cyclic hexapeptide core sequence (CFWKYC) while the N- and C-terminal regions are variable. UII, URP1, and URP2 mRNAs are differentially expressed within the central nervous system of teleost fishes, suggesting that they may exert distinct functions. Although the cardiovascular, ventilatory and locomotor effects of UII have been described in teleosts, much less is known regarding the physiological actions of URPs. The goal of the present study was to compare the central and peripheral actions of picomolar doses (5-500 pmol) of trout UII, URP1, and URP2 on cardio-ventilatory variables and locomotor activity in the unanesthetized trout. Compared to vehicle, intracerebroventricular injection of UII, URP1 and URP2 evoked a gradual increase in total ventilation (V TOT) reaching statistical significance for doses of 50 and 500 pmol of UII and URP1 but for only 500 pmol of URP2. In addition, UII, URP1 and URP2 provoked an elevation of dorsal aortic blood pressure (P DA) accompanied with tachycardia. All peptides caused an increase in locomotor activity (A CT), at a threshold dose of 5 pmol for UII and URP1, and 50 pmol for URP2. After intra-arterial (IA) injection, and in contrast to their central effects, only the highest dose of UII and URP1 significantly elevated V TOT and A CT. UII produced a dose-dependent hypertensive effect with concomitant bradycardia while URP1 increased P DA and heart rate after injection of only the highest dose of peptide. URP2 did not evoke any cardio-ventilatory or locomotor effect after IA injection. Collectively, these findings support the hypothesis that endogenous UII, URP1 and URP2 in the trout brain may act as neurotransmitters and/or neuromodulators acting synergistically or differentially to control the cardio-respiratory and locomotor systems. In the periphery, the only physiological actions of these peptides might be those related to the well-known cardiovascular regulatory actions of UII. It remains to determine whether the observed divergent physiological effects of UII and URPs are due to differential interaction with the UT receptor or binding to distinct UT subtypes.
Keywords: blood pressure; brain; heart rate; locomotor activity; trout; urotensin II; urotensin II-related peptides; ventilatory variables.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Central and Peripheral Effects of Urotensin II and Urotensin II-Related Peptides on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Trout.Front Neurosci. 2017 Feb 10;11:51. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00051. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28239335 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of peripherally administered urotensin II and arginine vasotocin on the QT interval of the electrocardiogram in trout.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 May-Jun;183-184:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26902806
-
Comparative distribution and in vitro activities of the urotensin II-related peptides URP1 and URP2 in zebrafish: evidence for their colocalization in spinal cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0119290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119290. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781313 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of gene/genome duplications on the evolution of the urotensin II and somatostatin families.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013 Jul 1;188:110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.12.015. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23313073 Review.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCII. Urotensin II, urotensin II-related peptide, and their receptor: from structure to function.Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(1):214-58. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009480. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25535277 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Effect of Central Administration of Urotensin II on Baroreflex and Blood Pressure in Conscious Normotensive Rabbits.Front Physiol. 2017 Feb 23;8:110. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00110. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28280470 Free PMC article.
-
Central and Peripheral Effects of Urotensin II and Urotensin II-Related Peptides on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Trout.Front Neurosci. 2017 Feb 10;11:51. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00051. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28239335 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prohormones and pituitary neuropeptides in the African cichlid, Astatotilapia burtoni.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 19;17(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2914-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27543050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bern H. A., Lederis K. (1969). A reference preparation for the study of active substances in the caudal neurosecretory system of teleosts. J. Endocrinol. 45 Suppl., xi–xii. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

