Epigenetic regulation in cancer progression
- PMID: 25949794
- PMCID: PMC4422217
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-45
Epigenetic regulation in cancer progression
Abstract
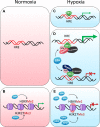
Cancer is a disease arising from both genetic and epigenetic modifications of DNA that contribute to changes in gene expression in the cell. Genetic modifications include loss or amplification of DNA, loss of heterozygosity (LOH) as well as gene mutations. Epigenetic changes in cancer are generally thought to be brought about by alterations in DNA and histone modifications that lead to the silencing of tumour suppressor genes and the activation of oncogenic genes. Other consequences that result from epigenetic changes, such as inappropriate expression or repression of some genes in the wrong cellular context, can also result in the alteration of control and physiological systems such that a normal cell becomes tumorigenic. Excessive levels of the enzymes that act as epigenetic modifiers have been reported as markers of aggressive breast cancer and are associated with metastatic progression. It is likely that this is a common contributor to the recurrence and spread of the disease. The emphasis on genetic changes, for example in genome-wide association studies and increasingly in whole genome sequencing analyses of tumours, has resulted in the importance of epigenetic changes having less attention until recently. Epigenetic alterations at both the DNA and histone level are increasingly being recognised as playing a role in tumourigenesis. Recent studies have found that distinct subgroups of poor-prognosis tumours lack genetic alterations but are epigenetically deregulated, pointing to the important role that epigenetic modifications and/or their modifiers may play in cancer. In this review, we highlight the multitude of epigenetic changes that can occur and will discuss how deregulation of epigenetic modifiers contributes to cancer progression. We also discuss the off-target effects that epigenetic modifiers may have, notably the effects that histone modifiers have on non-histone proteins that can modulate protein expression and activity, as well as the role of hypoxia in epigenetic regulation.
Keywords: Acetylation; Cancer; DNA methylation; Demethylation; Epigenetics; Histone modifications; Hypoxia; Transcription.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms in cancer.Postepy Biochem. 2018 Oct 15;64(2):148-156. doi: 10.18388/pb.2018_125. Postepy Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30656897 Review. English.
-
Epigenetics and cancer, 2nd IARC meeting, Lyon, France, 6 and 7 December 2007.Mol Oncol. 2008 Jun;2(1):33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.03.005. Epub 2008 Mar 27. Mol Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19383327 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3 lysine 4 acetylation and methylation dynamics define breast cancer subtypes.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5094-109. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6922. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26783963 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Modifying Enzymes in Gynaecological Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 16;13(4):816. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040816. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The importance of enhancer methylation for epigenetic regulation of tumorigenesis in squamous lung cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Jan;54(1):12-22. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00718-4. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34987166 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and Chemical Space Characterization of Inhibitors of the Epigenetic Target G9a: A Chemoinformatics Approach.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 11;8(33):30694-30704. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04566. eCollection 2023 Aug 22. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37636945 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations Interfere with Several Immune Components and Predict Poor Clinical Outcome.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 11;11(8):2254. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082254. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626750 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into regulatory RNAs in the cellular machinery.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Jun;56(6):1235-1249. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01239-6. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38871819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Epigenetic Symphony of Cancer: Insights and Epigenetic Therapies Implications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241250317. doi: 10.1177/15330338241250317. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38780251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones PA, Laird PW. Cancer-epigenetics comes of age. Nat Genet. 1999;21(2):163–167. - PubMed
-
- Dodge JE, Ramsahoye BH, Wo ZG, Okano M, Li E. De novo methylation of MMLV provirus in embryonic stem cells: CpG versus non-CpG methylation. Gene. 2002;289(1–2):41–48. - PubMed
-
- Okano M, Bell W, Haber DA, Li E. DNA Methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell. 1999;99(3):247–257. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

