NBM-T-BBX-OS01, Semisynthesized from Osthole, Induced G1 Growth Arrest through HDAC6 Inhibition in Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 25946558
- PMCID: PMC6272357
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20058000
NBM-T-BBX-OS01, Semisynthesized from Osthole, Induced G1 Growth Arrest through HDAC6 Inhibition in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
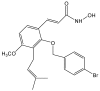
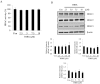
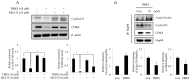
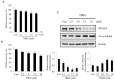
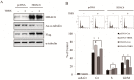
Disrupting lung tumor growth via histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibition is a strategy for cancer therapy or prevention. Targeting HDAC6 may disturb the maturation of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) mediated cell cycle regulation. In this study, we demonstrated the effects of semisynthesized NBM-T-BBX-OS01 (TBBX) from osthole on HDAC6-mediated growth arrest in lung cancer cells. The results exhibited that the anti-proliferative activity of TBBX in numerous lung cancer cells was more potent than suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), a clinically approved pan-HDAC inhibitor, and the growth inhibitory effect has been mediated through G1 growth arrest. Furthermore, the protein levels of cyclin D1, CDK2 and CDK4 were reduced while cyclin E and CDK inhibitor, p21Waf1/Cip1, were up-regulated in TBBX-treated H1299 cells. The results also displayed that TBBX inhibited HDAC6 activity via down-regulation HDAC6 protein expression. TBBX induced Hsp90 hyper-acetylation and led to the disruption of cyclin D1/Hsp90 and CDK4/Hsp90 association following the degradation of cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins through proteasome. Ectopic expression of HDAC6 rescued TBBX-induced G1 arrest in H1299 cells. Conclusively, the data suggested that TBBX induced G1 growth arrest may mediate HDAC6-caused Hsp90 hyper-acetylation and consequently increased the degradation of cyclin D1 and CDK4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Superior activity of a new histone deacetylase inhibitor (ZYJ-34c) in inhibiting growth of human leukemia cells by inducing p21WAF1 expression and cell cycle arrest.Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Aug;25(7):767-77. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000101. Anticancer Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24686006
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 22;280(29):26729-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500186200. Epub 2005 Jun 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15937340
-
Mechanism of cell cycle arrest caused by histone deacetylase inhibitors in human carcinoma cells.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2000 Oct;53(10):1191-200. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.53.1191. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2000. PMID: 11132966
-
Drugging the HDAC6-HSP90 interplay in malignant cells.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Oct;35(10):501-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25234862 Review.
-
Posttranslational modification and beyond: interplay between histone deacetylase 6 and heat-shock protein 90.Mol Med. 2021 Sep 16;27(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00375-3. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34530730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Off-target toxicity is a common mechanism of action of cancer drugs undergoing clinical trials.Sci Transl Med. 2019 Sep 11;11(509):eaaw8412. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw8412. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31511426 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel pyridine derivative with inhibitory activity against ovarian cancer progression in vivo and in vitro.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 18;13:1064485. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1064485. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36467091 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Diversity and Biochemical Content in Two Invasive Alien Species: Looking for Chemical Similarities and Bioactivities.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 22;21(1):5. doi: 10.3390/md21010005. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662178 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC11 mediates the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53 and inhibits the anti-leukemia effect of PD0166285.Med Oncol. 2023 Oct 7;40(11):325. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02196-2. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37805625
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor MPT0B291 suppresses Glioma Growth in vitro and in vivo partially through acetylation of p53.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 19;16(16):3184-3199. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45505. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33162824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steels E., Paesmans M., Berghmans T., Branle F., Lemaitre F., Mascaux C., Meert A.P., Vallot F., Lafitte J.J., Sculier J.P. Role of p53 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: A systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2001;18:705–719. doi: 10.1183/09031936.01.00062201. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraga M.F., Ballestar E., Paz M.F., Ropero S., Setien F., Ballestar M.L., Heine-Suner D., Cigudosa J.C., Urioste M., Benitez J., et al. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:10604–10609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500398102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

