Evolution of proteasome regulators in eukaryotes
- PMID: 25943340
- PMCID: PMC4453063
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evv068
Evolution of proteasome regulators in eukaryotes
Abstract
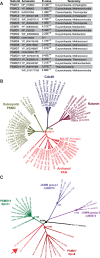
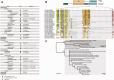
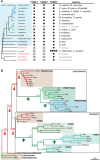
All living organisms require protein degradation to terminate biological processes and remove damaged proteins. One such machine is the 20S proteasome, a specialized barrel-shaped and compartmentalized multicatalytic protease. The activity of the 20S proteasome generally requires the binding of regulators/proteasome activators (PAs), which control the entrance of substrates. These include the PA700 (19S complex), which assembles with the 20S and forms the 26S proteasome and allows the efficient degradation of proteins usually labeled by ubiquitin tags, PA200 and PA28, which are involved in proteolysis through ubiquitin-independent mechanisms and PI31, which was initially identified as a 20S inhibitor in vitro. Unlike 20S proteasome, shown to be present in all Eukaryotes and Archaea, the evolutionary history of PAs remained fragmentary. Here, we made a comprehensive survey and phylogenetic analyses of the four types of regulators in 17 clades covering most of the eukaryotic supergroups. We found remarkable conservation of each PA700 subunit in all eukaryotes, indicating that the current complex PA700 structure was already set up in the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA). Also present in LECA, PA200, PA28, and PI31 showed a more contrasted evolutionary picture, because many lineages have subsequently lost one or two of them. The paramount conservation of PA700 composition in all eukaryotes and the dynamic evolution of PA200, PA28, and PI31 are discussed in the light of current knowledge on their physiological roles.
Keywords: PA200; PA28; PA700; PI31; evolution; proteasome.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The proteasome-dependent proteolytic system.Mol Biol Rep. 1999 Apr;26(1-2):3-9. doi: 10.1023/a:1006909522731. Mol Biol Rep. 1999. PMID: 10363639 Review.
-
Purification of PA700, the 19S regulatory complex of the 26S proteasome.Methods Enzymol. 2005;398:295-306. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)98024-5. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16275337
-
Comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of the 20S proteasome complex.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:187-236. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05009-3. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413316 Review.
-
Inhibition of Proteasome Activity Induces Formation of Alternative Proteasome Complexes.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 17;291(25):13147-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.717652. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129254 Free PMC article.
-
20S proteasome prevents aggregation of heat-denatured proteins without PA700 regulatory subcomplex like a molecular chaperone.Biomacromolecules. 2004 Jul-Aug;5(4):1465-9. doi: 10.1021/bm049957a. Biomacromolecules. 2004. PMID: 15244466
Cited by
-
Tumors escape immunosurveillance by overexpressing the proteasome activator PSME3.Oncoimmunology. 2020 May 21;9(1):1761205. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1761205. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32923122 Free PMC article.
-
Gates, Channels, and Switches: Elements of the Proteasome Machine.Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Jan;41(1):77-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.10.009. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 26643069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating Proteasome Activity.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 23;12(3):343. doi: 10.3390/biom12030343. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327535 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System Is a Key Regulator of Pluripotent Stem Cell Survival and Motor Neuron Differentiation.Cells. 2019 Jun 13;8(6):581. doi: 10.3390/cells8060581. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31200561 Free PMC article.
-
Proteostasis, oxidative stress and aging.Redox Biol. 2017 Oct;13:550-567. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28763764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D. ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2104–2105. - PubMed
-
- Bachvaroff TR, Handy SM, Place AR, Delwiche CF. Alveolate phylogeny inferred using concatenated ribosomal proteins. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2011;58:223–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

