Regulation of phagocytosis by Rho GTPases
- PMID: 25941749
- PMCID: PMC4601285
- DOI: 10.4161/21541248.2014.989785
Regulation of phagocytosis by Rho GTPases
Abstract
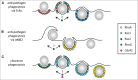
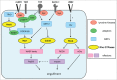
Phagocytosis is defined as a cellular uptake pathway for particles of greater than 0.5 μm in diameter. Particle clearance by phagocytosis is of critical importance for tissue health and homeostasis. The ultimate goal of anti-pathogen phagocytosis is to destroy engulfed bacteria or fungi and to stimulate cell-cell signaling that mount an efficient immune defense. In contrast, clearance phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cell debris is anti-inflammatory. High capacity clearance phagocytosis pathways are available to professional phagocytes of the immune system and the retina. Additionally, a low capacity, so-called bystander phagocytic pathway is available to most other cell types. Different phagocytic pathways are stimulated by particle ligation of distinct surface receptors but all forms of phagocytosis require F-actin recruitment beneath tethered particles and F-actin re-arrangement promoting engulfment, which are controlled by Rho family GTPases. The specificity of Rho GTPase activity during the different forms of phagocytosis by mammalian cells is the subject of this review.
Keywords: clearance; digestion; engulfment; f-actin recruitment; internalization; membrane receptors; phagocytic cup; phagosome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Function of Rho family proteins in actin dynamics during phagocytosis and engulfment.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;2(10):E191-6. doi: 10.1038/35036454. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11025683 Review.
-
Regulation of phagocytosis by Rho GTPases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;291:43-60. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27511-8_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981459 Review.
-
Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis requires CDC42 and Rac1.EMBO J. 1998 Nov 2;17(21):6219-29. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.21.6219. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9799231 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-kinase and myosin-II control phagocytic cup formation during CR, but not FcgammaR, phagocytosis.Curr Biol. 2002 Aug 20;12(16):1413-18. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01069-2. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12194823
-
Imaging flow cytometry and GST pulldown assays provide new insights into channel catfish leukocyte immune-type receptor-mediated phagocytic pathways.Dev Comp Immunol. 2017 Feb;67:126-138. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27984101
Cited by
-
Repurposing Treatments to Enhance Innate Immunity. Can Statins Improve Neutrophil Functions and Clinical Outcomes in COPD?J Clin Med. 2016 Oct 11;5(10):89. doi: 10.3390/jcm5100089. J Clin Med. 2016. PMID: 27727158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and functions of endocytosis in T cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Sep 9;19(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00766-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34503523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycation reaction and the role of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products in immunity and social behavior.Glycoconj J. 2021 Jun;38(3):303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10719-020-09956-6. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Glycoconj J. 2021. PMID: 33108607 Review.
-
Temporal changes in the microglial proteome of male and female mice after a diffuse brain injury using label-free quantitative proteomics.Glia. 2023 Apr;71(4):880-903. doi: 10.1002/glia.24313. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Glia. 2023. PMID: 36468604 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics revealed modulation of macrophages by MetQ gene of Streptococcus suis serotype 2.AMB Express. 2020 Oct 30;10(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01131-2. AMB Express. 2020. PMID: 33125582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Depraetere V. “Eat me” signals of apoptotic bodies. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2:E104; PMID:10854338 - PubMed
-
- Reddick LE, Alto NM. Bacteria fighting back: how pathogens target and subvert the host innate immune system. Mol Cell 2014; 54:321-8; PMID:24766896; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- deCathelineau AM,Henson PM. The final step in programmed cell death: phagocytes carry apoptotic cells to the grave. Essays Biochem 2003; 39:105-17; PMID:14585077 - PubMed
-
- Rothlin CV, Ghosh S, Zuniga EI, Oldstone MB, Lemke G. TAM receptors are pleiotropic inhibitors of the innate immune response. Cell 2007; 131:1124-36; PMID:18083102; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.034 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Henson PM. Dampening inflammation. Nat Immunol 2005; 6:1179-81; PMID:16369556 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
