Physical exercise enhances cognitive flexibility as well as astrocytic and synaptic markers in the medial prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 25938418
- PMCID: PMC4418599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124859
Physical exercise enhances cognitive flexibility as well as astrocytic and synaptic markers in the medial prefrontal cortex
Abstract
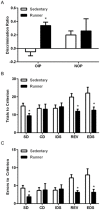
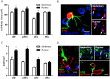
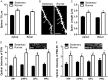
Physical exercise enhances a wide range of cognitive functions in humans. Running-induced cognitive enhancement has also been demonstrated in rodents but with a strong emphasis on tasks that require the hippocampus. Additionally, studies designed to identify mechanisms that underlie cognitive enhancement with physical exercise have focused on running-induced changes in neurons with little attention paid to such changes in astrocytes. To further our understanding of how the brain changes with physical exercise, we investigated whether running alters performance on cognitive tasks that require the prefrontal cortex and whether any such changes are associated with astrocytic, as well as neuronal, plasticity. We found that running enhances performance on cognitive tasks known to rely on the prefrontal cortex. By contrast, we found no such improvement on a cognitive task known to rely on the perirhinal cortex. Moreover, we found that running enhances synaptic, dendritic and astrocytic measures in several brain regions involved in cognition but that changes in the latter measures were more specific to brain regions associated with cognitive improvements. These findings suggest that physical exercise induces widespread plasticity in both neuronal and nonneuronal elements and that both types of changes may be involved in running-induced cognitive enhancement.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sexual experience enhances cognitive flexibility and dendritic spine density in the medial prefrontal cortex.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Nov;125:73-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 26188276
-
Maternal deprivation induces deficits in temporal memory and cognitive flexibility and exaggerates synaptic plasticity in the rat medial prefrontal cortex.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Oct;98(3):207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22922490
-
Noradrenergic modulation of cognitive function in rat medial prefrontal cortex as measured by attentional set shifting capability.Neuroscience. 2006 Feb;137(3):1039-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.09.031. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16298081
-
Serotonin/dopamine interaction in memory formation.Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:603-23. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00928-X. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18772052 Review.
-
Functional basis of associative learning and its relationships with long-term potentiation evoked in the involved neural circuits: Lessons from studies in behaving mammals.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Oct;124:3-18. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25916668 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal neurochemicals are associated with exercise group and intensity, psychological health, and general cognition in older adults.Geroscience. 2023 Jun;45(3):1667-1685. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00719-9. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Geroscience. 2023. PMID: 36626020 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
TAF15 downregulation contributes to the benefits of physical training on dendritic spines and working memory in aged mice.Aging Cell. 2024 Sep;23(9):e14244. doi: 10.1111/acel.14244. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38874013 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characteristics and Coping Strategies among Rugby Athletes: A Cluster Analysis Approach.J Pers Med. 2024 Mar 9;14(3):292. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030292. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38541034 Free PMC article.
-
Running wheel exercise reduces renewal of extinguished instrumental behavior and alters medial prefrontal cortex neurons in adolescent, but not adult, rats.Behav Neurosci. 2017 Dec;131(6):460-469. doi: 10.1037/bne0000218. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29083204 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological effects of aerobic exercise, with a focus on patients with schizophrenia.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Aug;269(5):499-515. doi: 10.1007/s00406-019-01025-w. Epub 2019 May 21. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31115660 Review.
References
-
- Kramer AF, Erickson KI. Capitalizing on cortical plasticity: influence of physical activity on cognition and brain function. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007;11: 342–348. - PubMed
-
- Salis AS. Proactive and reactive effects of vigorous exercise on learning and vocabulary comprehension. Percept Mot Skills. 2013;116: 918–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

