Towards the identification of the loci of adaptive evolution
- PMID: 25937885
- PMCID: PMC4409029
- DOI: 10.1111/2041-210X.12324
Towards the identification of the loci of adaptive evolution
Abstract
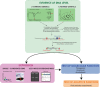
1. Establishing the genetic and molecular basis underlying adaptive traits is one of the major goals of evolutionary geneticists in order to understand the connection between genotype and phenotype and elucidate the mechanisms of evolutionary change. Despite considerable effort to address this question, there remain relatively few systems in which the genes shaping adaptations have been identified. 2. Here, we review the experimental tools that have been applied to document the molecular basis underlying evolution in several natural systems, in order to highlight their benefits, limitations and suitability. In most cases, a combination of DNA, RNA and functional methodologies with field experiments will be needed to uncover the genes and mechanisms shaping adaptation in nature.
Keywords: DNA mapping; QTL; adaptation; candidate genes; expression; functional analysis; resequencing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of variation in lifespan using a multiparental advanced intercross Drosophila mapping population.BMC Genet. 2016 Aug 2;17:113. doi: 10.1186/s12863-016-0419-9. BMC Genet. 2016. PMID: 27485207 Free PMC article.
-
Flowering time QTL in natural populations of Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for their adaptive value.Mol Ecol. 2014 Sep;23(17):4291-303. doi: 10.1111/mec.12857. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Mol Ecol. 2014. PMID: 25039363
-
Quantitative trait locus analyses and the study of evolutionary process.Mol Ecol. 2004 Sep;13(9):2505-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02254.x. Mol Ecol. 2004. PMID: 15315666 Review.
-
The ongoing adaptive evolution of ASPM and Microcephalin is not explained by increased intelligence.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Mar 15;16(6):600-8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl487. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17220170
-
Quantitative genomics: exploring the genetic architecture of complex trait predisposition.J Anim Sci. 2004;82 E-Suppl:E300-312. doi: 10.2527/2004.8213_supplE300x. J Anim Sci. 2004. PMID: 15471811 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic regions of speciation and adaptation among three species of grouse.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 28;9(1):812. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36880-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30692562 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic basis for adaptive morphological variation in a threatened Aotearoa | New Zealand bird, the hihi (Notiomystis cincta).Proc Biol Sci. 2020 Aug 26;287(1933):20200948. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2020.0948. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Proc Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32842928 Free PMC article.
-
Genome scans for divergent selection in natural populations of the widespread hardwood species Eucalyptus grandis (Myrtaceae) using microsatellites.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 17;6:34941. doi: 10.1038/srep34941. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27748400 Free PMC article.
-
A large chromosomal inversion shapes gene expression in seaweed flies (Coelopa frigida).Evol Lett. 2021 Oct 7;5(6):607-624. doi: 10.1002/evl3.260. eCollection 2021 Dec. Evol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34917400 Free PMC article.
-
The phoenix hypothesis of speciation.Proc Biol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;289(1987):20221186. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.1186. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Proc Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36382528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abzhanov A, Kuo WP, Hartmann C, Grant BR, Grant PR. Tabin CJ. The calmodulin pathway and evolution of elongated beak morphology in Darwin's finches. Nature. 2006;442:563–567. - PubMed
-
- Abzhanov A, Extavour CG, Groover A, Hodges SA, Hoekstra HE, Kramer EM. Monteiro A. Are we there yet? Tracking the development of new model systems. Trends in Genetics. 2008;24:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Altshuler D, Pollara VJ, Cowles CR, Van Etten WJ, Baldwin J, Linton L. Lander ES. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature. 2000;407:513–516. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
