An Apela RNA-Containing Negative Feedback Loop Regulates p53-Mediated Apoptosis in Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 25936916
- PMCID: PMC4458197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.04.002
An Apela RNA-Containing Negative Feedback Loop Regulates p53-Mediated Apoptosis in Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
Maintaining genomic integrity is of paramount importance to embryonic stem cells (ESCs), as mutations are readily propagated to daughter cells. ESCs display hypersensitivity to DNA damage-induced apoptosis (DIA) to prevent such propagation, although the molecular mechanisms underlying this apoptotic response are unclear. Here, we report that the regulatory RNA Apela positively regulates p53-mediated DIA. Apela is highly expressed in mouse ESCs and is repressed by p53 activation, and Apela depletion compromises p53-dependent DIA. Although Apela contains a coding region, this coding ability is dispensable for Apela's role in p53-mediated DIA. Instead, Apela functions as a regulatory RNA and interacts with hnRNPL, which prevents the mitochondrial localization and activation of p53. Together, these results describe a tri-element negative feedback loop composed of p53, Apela, and hnRNPL that regulates p53-mediated DIA, and they further demonstrate that regulatory RNAs add a layer of complexity to the apoptotic response of ESCs after DNA damage.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
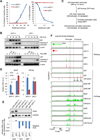
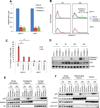

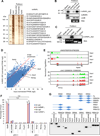
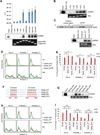
Similar articles
-
p53 and p73 Regulate Apoptosis but Not Cell-Cycle Progression in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells upon DNA Damage and Differentiation.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Dec 13;7(6):1087-1098. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27866875 Free PMC article.
-
Sall4 Guides p53-Mediated Enhancer Interference upon DNA Damage in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells.Stem Cells. 2022 Nov 29;40(11):1008-1019. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac058. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35977539
-
Lnc956 regulates mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation in response to DNA damage in a p53-independent pathway.Sci Adv. 2023 Jan 20;9(3):eade9742. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade9742. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 36662856 Free PMC article.
-
The p53 Family Coordinates Wnt and Nodal Inputs in Mesendodermal Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Jan 5;20(1):70-86. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 27889317 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal stress induces 2-cell embryo-like state transition of the mouse ESCs through p53 activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Nov 19;579:175-180. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.068. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34607171
Cited by
-
Conserved role of hnRNPL in alternative splicing of epigenetic modifiers enables B cell activation.EMBO Rep. 2024 Jun;25(6):2662-2697. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00152-3. Epub 2024 May 14. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38744970 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and functional implications of the renal apelinergic system in rodents.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 17;12(8):e0183094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183094. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28817612 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of APLN and APELA in the physiology and pathology of the female reproductive system.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 11;8:e10245. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10245. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240613 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid oxidation is required for embryonic stem cell survival during metabolic stress.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e52122. doi: 10.15252/embr.202052122. Epub 2021 May 5. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33950553 Free PMC article.
-
The Apelinergic System: Apelin, ELABELA, and APJ Action on Cell Apoptosis: Anti-Apoptotic or Pro-Apoptotic Effect?Cells. 2022 Dec 30;12(1):150. doi: 10.3390/cells12010150. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611944 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:1106–1117. - PubMed
-
- Chng SC, Ho L, Tian J, Reversade B. ELABELA: a hormone essential for heart development signals via the apelin receptor. Dev Cell. 2013;27:672–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

