Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 25922072
- PMCID: PMC4463461
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628164
Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
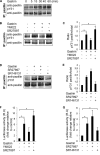
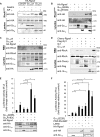
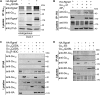
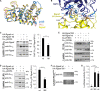
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Rgnef (also known as ArhGEF28 or p190RhoGEF) promotes colon carcinoma cell motility and tumor progression via interaction with focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Mechanisms of Rgnef activation downstream of integrin or G protein-coupled receptors remain undefined. In the absence of a recognized G protein signaling homology domain in Rgnef, no proximal linkage to G proteins was known. Utilizing multiple methods, we have identified Rgnef as a new effector for Gα13 downstream of gastrin and the type 2 cholecystokinin receptor. In DLD-1 colon carcinoma cells depleted of Gα13, gastrin-induced FAK Tyr(P)-397 and paxillin Tyr(P)-31 phosphorylation were reduced. RhoA GTP binding and promoter activity were increased by Rgnef in combination with active Gα13. Rgnef co-immunoprecipitated with activated Gα13Q226L but not Gα12Q229L. The Rgnef C-terminal (CT, 1279-1582) region was sufficient for co-immunoprecipitation, and Rgnef-CT exogenous expression prevented Gα13-stimulated SRE activity. A domain at the C terminus of the protein close to the FAK binding domain is necessary to bind to Gα13. Point mutations of Rgnef-CT residues disrupt association with active Gα13 but not Gαq. These results show that Rgnef functions as an effector of Gα13 signaling and that this linkage may mediate FAK activation in DLD-1 colon carcinoma cells.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); Gastrin; cell signaling; guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF); heterotrimeric G protein; regulator of G protein signaling.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p190RhoGEF (Rgnef) promotes colon carcinoma tumor progression via interaction with focal adhesion kinase.Cancer Res. 2011 Jan 15;71(2):360-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2894. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21224360 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phospholipase Cgamma1 in cell spreading requires association with a beta-Pix/GIT1-containing complex, leading to activation of Cdc42 and Rac1.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(16):5790-805. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00778-07. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17562871 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Intermittent fasting from dawn to sunset for 30 consecutive days is associated with anticancer proteomic signature and upregulates key regulatory proteins of glucose and lipid metabolism, circadian clock, DNA repair, cytoskeleton remodeling, immune system and cognitive function in healthy subjects.J Proteomics. 2020 Apr 15;217:103645. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103645. Epub 2020 Jan 9. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31927066 Free PMC article.
-
A Gα12-specific Binding Domain in AKAP-Lbc and p114RhoGEF.J Mol Signal. 2016 Sep 9;11:3. doi: 10.5334/1750-2187-11-3. J Mol Signal. 2016. PMID: 31051012 Free PMC article.
-
Inclusion Formation and Toxicity of the ALS Protein RGNEF and Its Association with the Microtubule Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 5;21(16):5597. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165597. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32764283 Free PMC article.
-
Gα12 and Gα13: Versatility in Physiology and Pathology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 14;10:809425. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.809425. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35237598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARHGEF3 regulates the stability of ACLY to promote the proliferation of lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Oct 14;13(10):870. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05297-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36241648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaffe A. B., Hall A. (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 247–269 - PubMed
-
- Sahai E., Marshall C. J. (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 133–142 - PubMed
-
- Leve F., Morgado-Díaz J. A. (2012) Rho GTPase signaling in the development of colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 113, 2549–2559 - PubMed
-
- van Horck F. P., Ahmadian M. R., Haeusler L. C., Moolenaar W. H., Kranenburg O. (2001) Characterization of p190RhoGEF, a RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor that interacts with microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4948–4956 - PubMed
-
- Lim Y., Lim S.-T., Tomar A., Gardel M., Bernard-Trifilo J. A., Chen X. L., Uryu S. A., Canete-Soler R., Zhai J., Lin H., Schlaepfer W. W., Nalbant P., Bokoch G., Ilic D., Waterman-Storer C., Schlaepfer D. D. (2008) PyK2 and FAK connections to p190Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor regulate RhoA activity, focal adhesion formation, and cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 180, 187–203 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

