The Toluene o-Xylene Monooxygenase Enzymatic Activity for the Biosynthesis of Aromatic Antioxidants
- PMID: 25915063
- PMCID: PMC4411060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124427
The Toluene o-Xylene Monooxygenase Enzymatic Activity for the Biosynthesis of Aromatic Antioxidants
Abstract
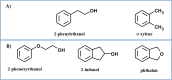
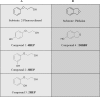
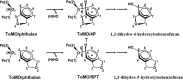
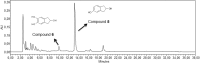
Monocyclic phenols and catechols are important antioxidant compounds for the food and pharmaceutic industries; their production through biotransformation of low-added value starting compounds is of major biotechnological interest. The toluene o-xylene monooxygenase (ToMO) from Pseudomonas sp. OX1 is a bacterial multicomponent monooxygenase (BMM) that is able to hydroxylate a wide array of aromatic compounds and has already proven to be a versatile biochemical tool to produce mono- and dihydroxylated derivatives of aromatic compounds. The molecular determinants of its regioselectivity and substrate specificity have been thoroughly investigated, and a computational strategy has been developed which allows designing mutants able to hydroxylate non-natural substrates of this enzyme to obtain high-added value compounds of commercial interest. In this work, we have investigated the use of recombinant ToMO, expressed in cells of Escherichia coli strain JM109, for the biotransformation of non-natural substrates of this enzyme such as 2-phenoxyethanol, phthalan and 2-indanol to produce six hydroxylated derivatives. The hydroxylated products obtained were identified, isolated and their antioxidant potential was assessed both in vitro, using the DPPH assay, and on the rat cardiomyoblast cell line H9c2. Incubation of H9c2 cells with the hydroxylated compounds obtained from ToMO-catalyzed biotransformation induced a differential protective effect towards a mild oxidative stress induced by the presence of sodium arsenite. The results obtained confirm once again the versatility of the ToMO system for oxyfunctionalization reactions of biotechnological importance. Moreover, the hydroxylated derivatives obtained possess an interesting antioxidant potential that encourages the use of the enzyme for further functionalization reactions and their possible use as scaffolds to design novel bioactive molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuning the specificity of the recombinant multicomponent toluene o-xylene monooxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain OX1 for the biosynthesis of tyrosol from 2-phenylethanol.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Aug;77(15):5428-37. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00461-11. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21666013 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of the regioselectivity of toluene/o-xylene monooxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain OX1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Feb;75(3):823-36. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01951-08. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19074607 Free PMC article.
-
Regiospecificity of two multicomponent monooxygenases from Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1: molecular basis for catabolic adaptation of this microorganism to methylated aromatic compounds.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Aug;71(8):4736-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4736-4743.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16085870 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate trafficking and dioxygen activation in bacterial multicomponent monooxygenases.Acc Chem Res. 2007 Jul;40(7):466-74. doi: 10.1021/ar600040e. Epub 2007 May 23. Acc Chem Res. 2007. PMID: 17518435 Review.
-
Biotransformation: a green and efficient way of antioxidant synthesis.Free Radic Res. 2016 Sep;50(9):939-48. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2016.1209745. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Free Radic Res. 2016. PMID: 27383446 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Supplementation in the Treatment of Aging-Associated Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Feb 12;7:24. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00024. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26903869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Phthalan and Coumaran Chemistry.ChemistryOpen. 2018 Nov 23;7(11):914-929. doi: 10.1002/open.201800184. eCollection 2018 Nov. ChemistryOpen. 2018. PMID: 30498677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and Biotechnological Synthesis of Hydroxytyrosol.Foods. 2024 May 28;13(11):1694. doi: 10.3390/foods13111694. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38890922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Peroxodiiron(III/III) Intermediate Mediating Both N-Hydroxylation Steps in Biosynthesis of the N-Nitrosourea Pharmacophore of Streptozotocin by the Multi-domain Metalloenzyme SznF.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jul 8;142(27):11818-11828. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c03431. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32511919 Free PMC article.
-
Denatured lysozyme-coated carbon nanotubes: a versatile biohybrid material.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 12;9(1):16643. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52701-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31719550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A, Gupta S, Sharma RK. Role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Reprod. Biol Endocrinol. 2005;3:28–48. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1215514/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004;55:373–399. Available: http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.1.... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marco S, Rullo R, Albino A, Masullo M, De Vendittis E, Amato M. The thioredoxin system in the dental caries pathogen Streptococcus mutans and the food-industry bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus. Biochimie. 2013;95(11):2145–56. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23954859. 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.08.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stressful initiations. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3227–34. Available: http://jcs.biologists.org/content/115/16/3227.long. - PubMed
-
- Conti V, Corbi G, Russomanno G, Simeon V, Ferrara N, Filippelli W, et al. Oxidative stress effects on endothelial cells treated with different athletes' sera. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012; 44(1):39–49. Available: http://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2012&iss.... 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318227f69c - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

