Imprinted expression in cystic embryoid bodies shows an embryonic and not an extra-embryonic pattern
- PMID: 25912690
- PMCID: PMC4454777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.04.010
Imprinted expression in cystic embryoid bodies shows an embryonic and not an extra-embryonic pattern
Abstract
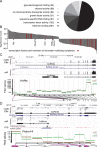
A large subset of mammalian imprinted genes show extra-embryonic lineage (EXEL) specific imprinted expression that is restricted to placental trophectoderm lineages and to visceral yolk sac endoderm (ysE). Isolated ysE provides a homogenous in vivo model of a mid-gestation extra-embryonic tissue to examine the mechanism of EXEL-specific imprinted gene silencing, but an in vitro model of ysE to facilitate more rapid and cost-effective experiments is not available. Reports indicate that ES cells differentiated into cystic embryoid bodies (EBs) contain ysE, so here we investigate if cystic EBs model ysE imprinted expression. The imprinted expression pattern of cystic EBs is shown to resemble fetal liver and not ysE. To investigate the reason for this we characterized the methylome and transcriptome of cystic EBs in comparison to fetal liver and ysE, by whole genome bisulphite sequencing and RNA-seq. Cystic EBs show a fetal liver pattern of global hypermethylation and low expression of repeats, while ysE shows global hypomethylation and high expression of IAPEz retroviral repeats, as reported for placenta. Transcriptome analysis confirmed that cystic EBs are more similar to fetal liver than ysE and express markers of early embryonic endoderm. Genome-wide analysis shows that ysE shares epigenetic and repeat expression features with placenta. Contrary to previous reports, we show that cystic EBs do not contain ysE, but are more similar to the embryonic endoderm of fetal liver. This explains why cystic EBs reproduce the imprinted expression seen in the embryo but not that seen in the ysE.
Keywords: Cystic embryoid bodies (EBs); DNA methylation; Genomic imprinting; Visceral endoderm (VE); Visceral yolk sac (VYS); Visceral yolk sac Endoderm (ysE).
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extra-embryonic-specific imprinted expression is restricted to defined lineages in the post-implantation embryo.Dev Biol. 2011 May 15;353(2):420-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.02.017. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21354127 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of histone modifications and Gata6 gene expression induced by maternal diet in mouse embryoid bodies in a model of developmental programming.BMC Dev Biol. 2015 Jan 21;15:3. doi: 10.1186/s12861-015-0053-1. BMC Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25609498 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF and IHH rescue definitive hematopoiesis in Gata-4 and Gata-6-deficient murine embryoid bodies.Exp Hematol. 2009 Sep;37(9):1038-53. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2009.05.011. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Exp Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19501129 Free PMC article.
-
Is extra-embryonic endoderm a source of placental blood cells?Exp Hematol. 2020 Sep;89:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2020.07.008. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Exp Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32735907 Review.
-
Imprinting of the mouse Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998 May 25;140(1-2):9-14. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00022-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9722161 Review.
Cited by
-
Human iPS-derived pre-epicardial cells direct cardiomyocyte aggregation expansion and organization in vitro.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 17;12(1):4997. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24921-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34404774 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the mouse Allelome reveals tissue-specific regulation of allelic expression.Elife. 2017 Aug 14;6:e25125. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25125. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28806168 Free PMC article.
-
The Airn lncRNA does not require any DNA elements within its locus to silence distant imprinted genes.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jul 22;15(7):e1008268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008268. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31329595 Free PMC article.
-
JAZF1-SUZ12 dysregulates PRC2 function and gene expression during cell differentiation.Cell Rep. 2022 May 31;39(9):110889. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110889. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35649353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K., Niwa H., Iwase K., Takiguchi M., Mori M., Abe S.I., Yamamura K.I. Endoderm-specific gene expression in embryonic stem cells differentiated to embryoid bodies. Exp. Cell Res. 1996;229:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Antonchuk J. Formation of embryoid bodies from human pluripotent stem cells using AggreWell plates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;946:523–533. - PubMed
-
- Barlow D.P., Bartolomei M.S. Genomic imprinting in mammals. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014;6(2) http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018382, pii: a018382. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

