MicroRNA transcriptomes of distinct human NK cell populations identify miR-362-5p as an essential regulator of NK cell function
- PMID: 25909817
- PMCID: PMC4408982
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09993
MicroRNA transcriptomes of distinct human NK cell populations identify miR-362-5p as an essential regulator of NK cell function
Abstract
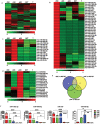
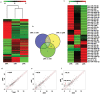
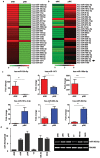
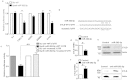
Natural killer (NK) cells are critical effectors in the immune response against malignancy and infection, and microRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in NK cell biology. Here we examined miRNA profiles of human NK cells from different cell compartments (peripheral blood, cord blood, and uterine deciduas) and of NKT and T cells from peripheral blood, and we identified a novel miRNA, miR-362-5p, that is highly expressed in human peripheral blood NK (pNK) cells. We also demonstrated that CYLD, a negative regulator of NF-κB signaling, was a target of miR-362-5p in NK cells. Furthermore, we showed that the over-expression of miR-362-5p enhanced the expression of IFN-γ, perforin, granzyme-B, and CD107a in human primary NK cells, and we found that silencing CYLD with a small interfering RNA (siRNA) mirrored the effect of miR-362-5p over-expression. In contrast, the inhibition of miR-362-5p had the opposite effect in NK cells, which was abrogated by CYLD siRNA, suggesting that miR-362-5p promotes NK-cell function, at least in part, by the down-regulation of CYLD. These results provide a resource for studying the roles of miRNAs in human NK cell biology and contribute to a better understanding of the physiologic significance of miRNAs in the regulation of NK cell function.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated mRNA-microRNA profiling of human NK cell differentiation identifies MiR-583 as a negative regulator of IL2Rγ expression.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 14;9(10):e108913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108913. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25313504 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-362-5p promotes tumor growth and metastasis by targeting CYLD in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):809-18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.041. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25449782
-
Regulation of Human Natural Killer Cell IFN-γ Production by MicroRNA-146a via Targeting the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 9;9:293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00293. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29593706 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
microRNA management of NK-cell developmental and functional programs.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Oct;44(10):2862-8. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444798. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25142111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-1224 contributes to ischemic stroke-mediated natural killer cell dysfunction by targeting Sp1 signaling.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jun 12;18(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02181-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34118948 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Pleiotropic Regulators in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 1;9:2491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02491. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30443251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique metabolism and protein expression signature in human decidual NK cells.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1136652. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1136652. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936959 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging insights into natural killer cells in human peripheral tissues.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Apr 28;16(5):310-20. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.34. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27121652 Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Dictating Eradication of Cancer by Natural Killer Cells.Trends Cancer. 2018 Aug;4(8):553-566. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Trends Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30064663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Di Santo J. P. Natural killer cell developmental pathways: a question of balance. Annu Rev Immunol. 24, 257–286 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama W. M., Kim S., & French A. R. The dynamic life of natural killer cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 405–429 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Smyth M. J., Hayakawa Y., Takeda K., Yagita H. New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2, 850–861(2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

