Suppression of glioblastoma by targeting the overactivated protein neddylation pathway
- PMID: 25904638
- PMCID: PMC4578582
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nov066
Suppression of glioblastoma by targeting the overactivated protein neddylation pathway
Abstract
Background: The neddylation pathway has been recently identified as an attractive anticancer target, and MLN4924, a specific NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, has been developed as a first-in-class anticancer agent. However, neither the status of the neddylation pathway in glioblastoma (GBM) nor the effect of MLN4924 against GBM has been systematically investigated yet.
Methods: To measure the activation state of the neddylation pathway in GBM, expression of the NEDD8-activating enzyme (E1), NEDD8-conjugating enzyme (E2), and global protein neddylation in GBM tumor tissues versus adjacent tissues were examined by immunoblotting analysis and immunohistochemistry staining. To assess the therapeutic efficacy of neddylation inhibition in GBM, cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo were determined upon neddylation inhibition by MLN4924, an investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor.
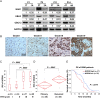
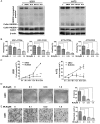
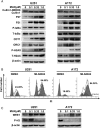
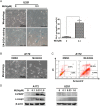
Results: The neddylation pathway was overactivated in a majority of GBM tumor tissues when compared with adjacent normal tissues. The upregulation of this pathway in GBM tissues was positively correlated with high-grade disease and postoperative recurrence but was negatively associated with patient overall survival. MLN4924 treatment inhibited cullin neddylation, inactivated cullin-RING E3 ligase, and led to the accumulation of tumor-suppressive cullin-RING E3 ligase substrates to trigger cell-cycle arrest and senescence or apoptosis in a cell-line dependent manner. Moreover, inhibition of neddylation by MLN4924 significantly suppressed tumor growth in an orthotopic xenograft model of human GBM.
Conclusion: Our study indicates that an overactivated neddylation pathway may be involved in GBM progression and that inhibition of this oncogenic pathway is a potentially new therapeutic approach for GBM.
Keywords: MLN4924; NEDD8; cullin-RING E3 ligase; glioblastoma; neddylation.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neddylation in glioblastomas.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):1305-6. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov165. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26395059 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Overactivated neddylation pathway as a therapeutic target in lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 May 22;106(6):dju083. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju083. Print 2014 Jun. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 24853380
-
Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 11;6:24218. doi: 10.1038/srep24218. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27063292 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(3):420-9. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1003003. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25782162 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Dec 10;21(17):2383-400. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5795. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24410571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Protein Neddylation for Cancer Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1217:297-315. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1025-0_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31898235 Review.
Cited by
-
MLN4924 suppresses neddylation and induces cell cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45263-45274. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9481. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27223074 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Conjugation of NEDD8 to the N-Terminus of a Model Protein Can Induce Degradation.Cells. 2021 Apr 9;10(4):854. doi: 10.3390/cells10040854. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33918652 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation suppression by a macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticle promotes dual immunomodulatory repair of diabetic wounds.Bioact Mater. 2024 Jan 6;34:366-380. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.12.025. eCollection 2024 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38269308 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation Regulates Macrophages and Implications for Cancer Therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 7;9:681186. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.681186. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34164400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Konglund A, Helseth R, Lund-Johansen M, et al. Surgery for high-grade gliomas in the aging. Acta Neurol Scand. 2013;128(3):185–193. - PubMed
-
- Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, et al. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 2012;379(9830):1984–1996. - PubMed
-
- Murphy M, Parney IF. Clinical trials in neurosurgical oncology. J Neurooncol. 2014;119(3):569–576. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A. Basic Medical Research Award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med. 2000;6(10):1073–1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

