Functional characterization of a cystatin from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides
- PMID: 25889816
- PMCID: PMC4352250
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-015-0725-5
Functional characterization of a cystatin from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides
Abstract
Background: Ticks and tick-borne diseases affect animal and human health worldwide and cause significant economic losses in the animal industry. Functional molecular research is important to understand the biological characteristics of ticks at the molecular level. Enzymes and enzyme inhibitory molecules play very important roles in tick physiology, and the cystatins are tight-binding inhibitors of papain-like cysteine proteases. To this end, a novel cystatin, designated RHcyst-1, was isolated from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides.
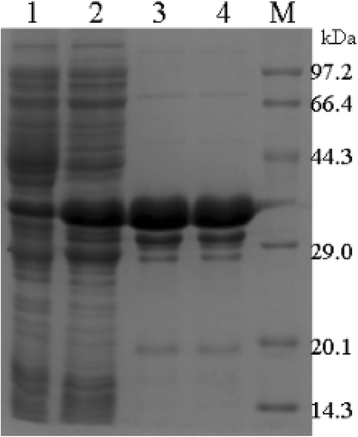
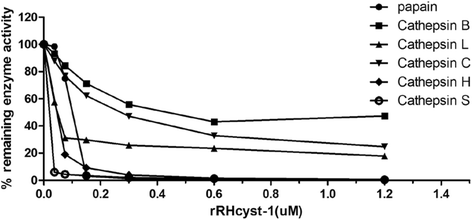
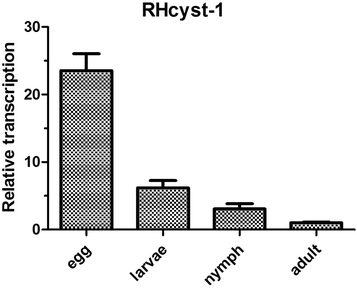
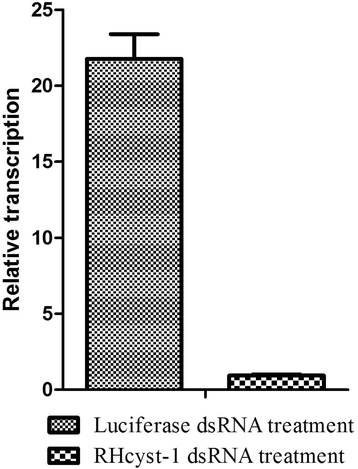
Methods: The full-length gene of RHcyst-1 was cloning by RACE. The recombinant protein of RHcyst-1 was expressed in a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fused soluble form in Escherichia coli, and its inhibitory activity against cathepsin L, B, C, H, and S, as well as papain, was identified by fluorogenic substrate analysis. Expression analysis of RHcyst-1 at different tick stages was performed by quantitative reverse transcription - PCR (qRT-PCR). An RNAi experiment for RHcyst-1 was performed to determine its function for tick physiology.
Results: The full-length cDNA of RHcyst-1 is 471 bp, including an intact open reading frame encoding an expected protein of 98 amino acids, without a signal peptide, having a predicted molecular weight of ~11 kDa and an isoelectric point of 5.66. A sequence analysis showed that it has significant homology with the known type 1 cystatins. The results of proteinase inhibition assays showed that rRHcyst-1 can effectively inhibit the six cysteine proteases' enzyme activities. An investigation of the RHcyst-1 genes' expression profile showed that it was more richly transcribed in the embryo (egg) stage. A disruption of the RHcyst-1 gene showed a significant decrease in the rate of tick hatching.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that RHcyst-1 may be involved in the early embryonic development of ticks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of a secreted cystatin from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides.Exp Appl Acarol. 2015 Oct;67(2):289-98. doi: 10.1007/s10493-015-9946-8. Epub 2015 Jul 19. Exp Appl Acarol. 2015. PMID: 26188856
-
A cysteine protease of Babesia microti and its interaction with tick cystatins.Parasitol Res. 2020 Sep;119(9):3013-3022. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06818-w. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32740752
-
Characterization of an intracellular cystatin homolog from the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis.Vet Parasitol. 2009 Mar 9;160(1-2):180-3. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.10.086. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Vet Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19091470
-
The role of cystatins in tick physiology and blood feeding.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012 Jun;3(3):117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012. PMID: 22647711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tick salivary protein Cystatin: structure, anti-inflammation and molecular mechanism.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024 Mar;15(2):102289. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2023.102289. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024. PMID: 38070274 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and function of a novel cystatin gene in the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus.Biol Open. 2019 Sep 18;8(9):bio042655. doi: 10.1242/bio.042655. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31511247 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of protein interactions between Eimeria maxima sporozoites and chicken jejunal epithelial cells by shotgun LC-MS/MS.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Apr 4;11(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2818-4. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29618377 Free PMC article.
-
Protease Inhibitors in Tick Saliva: The Role of Serpins and Cystatins in Tick-host-Pathogen Interaction.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 29;7:216. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00216. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28611951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a Novel Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from Poultry Red Mites: Potential Vaccine for Chickens.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;9(12):1472. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121472. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960218 Free PMC article.
-
Draft genome sequences of Hirudo medicinalis and salivary transcriptome of three closely related medicinal leeches.BMC Genomics. 2020 Apr 29;21(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6748-0. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32349672 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

