Fgf signaling controls the telencephalic distribution of Fgf-expressing progenitors generated in the rostral patterning center
- PMID: 25889070
- PMCID: PMC4416298
- DOI: 10.1186/s13064-015-0037-7
Fgf signaling controls the telencephalic distribution of Fgf-expressing progenitors generated in the rostral patterning center
Abstract
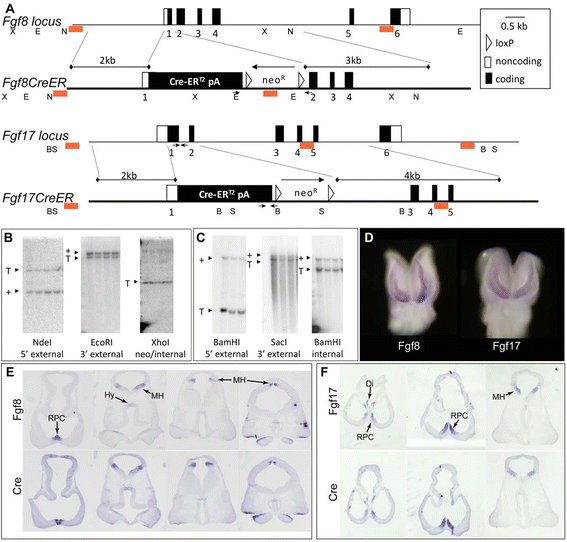
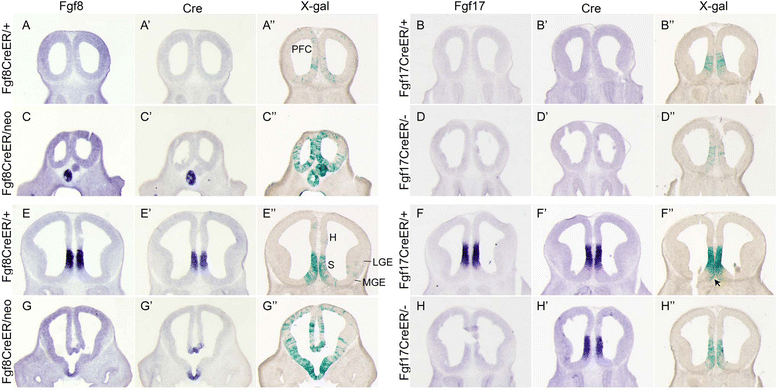
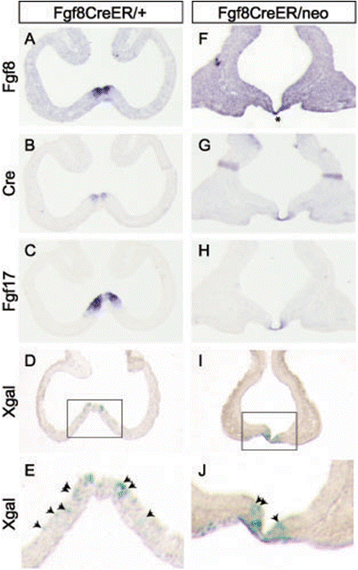
Background: The rostral patterning center (RPC) secretes multiple fibroblast growth factors (Fgfs) essential for telencephalon growth and patterning. Fgf expression patterns suggest that they mark functionally distinct RPC subdomains. We generated Fgf8(CreER) and Fgf17(CreER) mice and used them to analyze the lineages of Fgf8- versus Fgf17-expressing RPC cells.
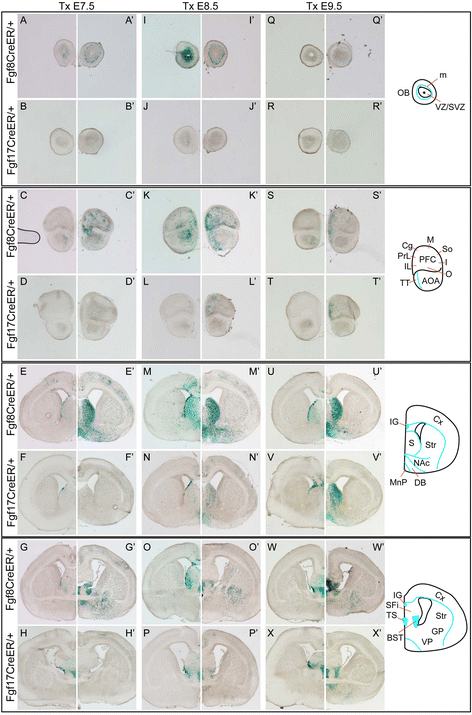
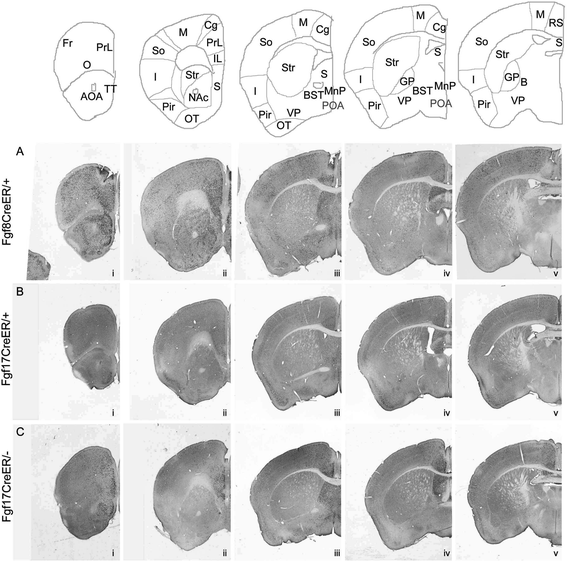
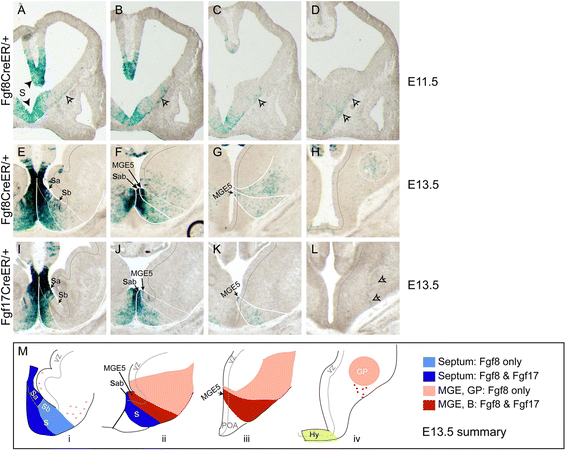
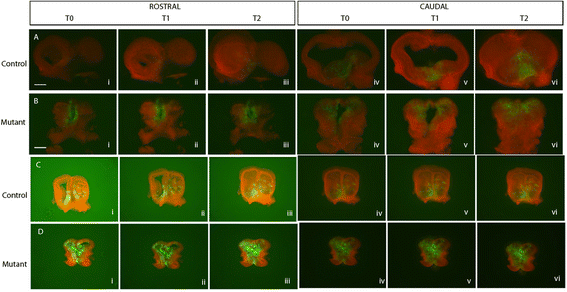
Results: Both lineages contributed to medial structures of the rostroventral telencephalon structures including the septum and medial prefrontral cortex. In addition, RPC-derived progenitors were observed in other regions of the early telencephalic neuroepithelium and generated neurons in the olfactory bulb, neocortex, and basal ganglia. Surprisingly, Fgf8(+) RPC progenitors generated the majority of basal ganglia cholinergic neurons. Compared to the Fgf8 lineage, the Fgf17 lineage was more restricted in its early dispersion and its contributions to the telencephalon. Mutant studies suggested that Fgf8 and Fgf17 restrict spread of RPC progenitor subpopulations.
Conclusions: We identified the RPC as an important source of progenitors that contribute broadly to the telencephalon and found that two molecularly distinct progenitor subtypes in the RPC make different contributions to the developing forebrain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGF15 promotes neurogenesis and opposes FGF8 function during neocortical development.Neural Dev. 2008 Jul 14;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-3-17. Neural Dev. 2008. PMID: 18625063 Free PMC article.
-
Ace/Fgf8 is required for forebrain commissure formation and patterning of the telencephalon.Development. 2000 Jun;127(12):2549-61. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.12.2549. Development. 2000. PMID: 10821754
-
Coordinate regulation and synergistic actions of BMP4, SHH and FGF8 in the rostral prosencephalon regulate morphogenesis of the telencephalic and optic vesicles.Neuroscience. 2002;111(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00616-9. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 11955708
-
Genetic patterning of the mammalian telencephalon by morphogenetic molecules and transcription factors.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006 Sep;78(3):256-66. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20077. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006. PMID: 17061260 Review.
-
The role of Fgf8 in telencephalic and diencephalic patterning.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009 Aug;20(6):719-25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.04.002. Epub 2009 Apr 10. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19596327 Review.
Cited by
-
Early perturbation of Wnt signaling reveals patterning and invagination-evagination control points in molar tooth development.Development. 2021 Jul 15;148(14):dev199685. doi: 10.1242/dev.199685. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Development. 2021. PMID: 34195802 Free PMC article.
-
Mispatterning and interneuron deficit in Tourette Syndrome basal ganglia organoids.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Dec;27(12):5007-5019. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01880-5. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36447010 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Transplantation for Alzheimer's Disease and Prospects for Generating Exogenic Neurons as a Source of Cells for Implantation.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231164712. doi: 10.1177/09636897231164712. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37219048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulation and Function of Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 and Its Function during Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neuron Development.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Sep 5;7:114. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00114. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27656162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single cell enhancer activity distinguishes GABAergic and cholinergic lineages in embryonic mouse basal ganglia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Apr 12;119(15):e2108760119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108760119. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35377797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimamura K, Rubenstein JL. Inductive interactions direct early regionalization of the mouse forebrain. Development. 1997;124(14):2709–18. - PubMed
-
- Shanmugalingam S, Houart C, Picker A, Reifers F, Macdonald R, Barth A, et al. Ace/Fgf8 is required for forebrain commissure formation and patterning of the telencephalon. Development. 2000;127(12):2549–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

