Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in human kidney transplants with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy
- PMID: 25884518
- PMCID: PMC4359521
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-015-0011-y
Kidney injury molecule-1 expression in human kidney transplants with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy
Abstract
Background: Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) is expressed in tubular epithelial cells after injury and may have a role in the development of renal graft fibrosis. In this study we evaluated the molecular and protein expressions of KIM-1 in dysfunctional allografts and also mRNA KIM-1 expression in urine as potential biomarkers of graft fibrosis.
Methods: Protein and mRNA levels in renal tissue and urinary sediment cells of 69 kidney transplant recipients that undertook for-cause graft biopsies were evaluated by immunohistochemistry and real-time polymerase chain reaction. The histopathology was classified according to the 2007 Banff schema.
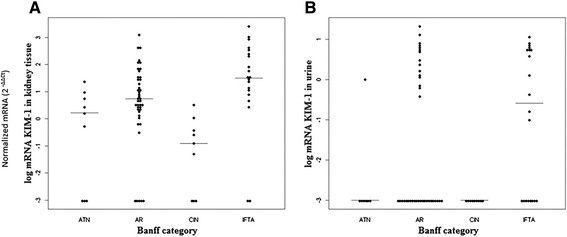
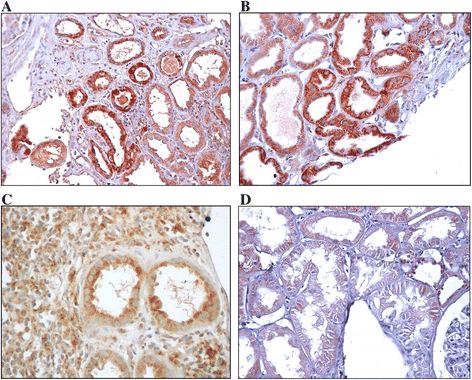
Results: KIM-1 protein expression was increased in biopsies with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA) compared with biopsies showing acute calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity (CIN) (P <0.05). Kidney tissue KIM-1 mRNA signaling (in) was increased in biopsies with IF/TA compared with all other groups (P <0.05). In the urine cells KIM-1 mRNA was also increased in patients with IF/TA compared with patients with acute CIN (P <0.05). Significant correlations were found between KIM-1 protein and mRNA levels in tissue, between mRNA expressions in tissue and urine and between protein tissue expression and gene expression in the urine.
Conclusions: KIM-1 seems to be a marker of kidney graft fibrosis. Urinary KIM-1 mRNA may become a useful non-invasive biomarker of the injuries that can trigger intra-graft fibrotic processes, such as interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noninvasive analyses of kidney injury molecule-1 messenger RNA in kidney transplant recipients with graft dysfunction.Transplant Proc. 2012 Oct;44(8):2297-9. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.07.047. Transplant Proc. 2012. PMID: 23026578
-
Expression of fibrosis-related genes in human renal allografts with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy.J Nephrol. 2013 Nov-Dec;26(6):1179-87. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000274. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23661587
-
Quantitative analyses of kidney injury molecule-1 messenger RNA in kidney transplant recipients with graft dysfunction.Transplant Proc. 2010 Mar;42(2):473-4. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.01.042. Transplant Proc. 2010. PMID: 20304168
-
Chronic allograft nephropathy or interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy: what is in a name?Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014 May;23(3):245-50. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000444811.26884.2d. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24626060 Review.
-
Diagnosis of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney allograft: implementation of microRNAs.Iran J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jan;8(1):4-12. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24413714 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Biomarkers Related to Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy among Kidney Transplant Recipients by mRNA-Sequencing.J Pers Med. 2023 Aug 10;13(8):1242. doi: 10.3390/jpm13081242. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37623492 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for individualized dosage adjustments in immunosuppressive therapy using calcineurin inhibitors after organ transplantation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Feb;40(2):151-159. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0070-2. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 29950613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of urinary kidney injury molecule-1, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, and N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase to predict chronic kidney disease progression and adverse outcomes.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Mar 30;50(5):e6106. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20176106. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 28380198 Free PMC article.
-
Alisol A 24-Acetate and Alisol B 23-Acetate Induced Autophagy Mediates Apoptosis and Nephrotoxicity in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 31;8:172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00172. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28408883 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1): a Multifunctional Glycoprotein and Biological Marker (Review).Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021;13(3):64-78. doi: 10.17691/stm2021.13.3.08. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021. PMID: 34603757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H, Hession CA, Cate RL, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4135–42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.7.4135. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

