Activating transcription factor 4 promotes angiogenesis of breast cancer through enhanced macrophage recruitment
- PMID: 25883982
- PMCID: PMC4391610
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/974615
Activating transcription factor 4 promotes angiogenesis of breast cancer through enhanced macrophage recruitment
Abstract
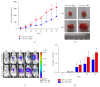
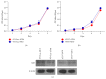
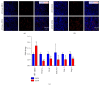
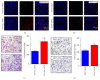
Angiogenesis plays an important role in the progression of tumor. Besides being regulated by tumor cells per se, tumor angiogenesis is also influenced by stromal cells in tumor microenvironment (TME), for example, tumor associated macrophages (TAMs). Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), a member of the ATF/CREB family, has been reported to be related to tumor angiogenesis. In this study, we found that exogenous overexpression of ATF4 in mouse breast cancer cells promotes tumor growth via increasing tumor microvascular density. However, ATF4 overexpression failed to increase the expression level of a series of proangiogenic factors including vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) in tumor cells in this model. Thus, we further investigated the infiltration of proangiogenic macrophages in tumor tissues and found that ATF4-overexpressing tumors could recruit more macrophages via secretion of macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF). Overall, we concluded that exogenous overexpression of ATF4 in breast cancer cells may facilitate the recruitment of macrophages into tumor tissues and promote tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth indirectly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breast tumor cell TACE-shed MCSF promotes pro-angiogenic macrophages through NF-κB signaling.Angiogenesis. 2014 Jul;17(3):573-85. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9405-2. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Angiogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24197832
-
Colony-stimulating factor-1 blockade by antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human mammary tumor xenografts in mice.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5378-84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0961. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289345
-
Osteopontin promotes vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent breast tumor growth and angiogenesis via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms.Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 1;68(1):152-61. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2126. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18172307
-
Target validation using RNA interference in solid tumors.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;361:227-38. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-208-4:227. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17172715 Review.
-
The possible mechanisms of tumor progression via CSF-1/CSF-1R pathway activation.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55(2 Suppl):501-6. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014. PMID: 25178319 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cellular immunity by activating transcription factor 4.Immunol Lett. 2020 Dec;228:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33002512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bioinformatic analysis found low expression and clinical significance of ATF4 in breast cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 12;10(2):e24669. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24669. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312639 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodegeneration: Keeping ATF4 on a Tight Leash.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Dec 15;11:410. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00410. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29326555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages: An important player in breast cancer progression.Thorac Cancer. 2022 Feb;13(3):269-276. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14268. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34914196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Mediated ATF4 Induction Promotes Survival in Detached Conditions in Metastatic Murine Mammary Cancer Cells.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:767479. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.767479. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847893 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

