An Integrated Molecular Analysis of Lung Adenocarcinomas Identifies Potential Therapeutic Targets among TTF1-Negative Tumors, Including DNA Repair Proteins and Nrf2
- PMID: 25878335
- PMCID: PMC4526428
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3286
An Integrated Molecular Analysis of Lung Adenocarcinomas Identifies Potential Therapeutic Targets among TTF1-Negative Tumors, Including DNA Repair Proteins and Nrf2
Abstract
Purpose: Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF1) immunohistochemistry (IHC) is used clinically to differentiate primary lung adenocarcinomas (LUAD) from squamous lung cancers and metastatic adenocarcinomas from other primary sites. However, a subset of LUAD (15%-20%) does not express TTF1, and TTF1-negative patients have worse clinical outcomes. As there are no established targeted agents with activity in TTF1-negative LUAD, we performed an integrated molecular analysis to identify potential therapeutic targets.
Experimental design: Using two clinical LUAD cohorts (274 tumors), one from our institution (PROSPECT) and The Cancer Genome Atlas, we interrogated proteomic profiles (by reverse phase protein array, RPPA), gene expression, and mutational data. Drug response data from 74 cell lines were used to validate potential therapeutic agents.
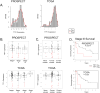
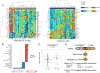
Results: Strong correlations were observed between TTF1 IHC and TTF1 measurements by RPPA (Rho = 0.57, P < 0.001) and gene expression (NKX2-1, Rho = 0.61, P < 0.001). Established driver mutations (e.g., BRAF and EGFR) were associated with high TTF1 expression. In contrast, TTF1-negative LUAD had a higher frequency of inactivating KEAP1 mutations (P = 0.001). Proteomic profiling identified increased expression of DNA repair proteins (e.g., Chk1 and the DNA repair score) and suppressed PI3k/mTOR signaling among TTF1-negative tumors, with differences in total proteins confirmed at the mRNA level. Cell line analysis showed drugs targeting DNA repair to be more active in TTF1-low cell lines.
Conclusions: Combined genomic and proteomic analyses demonstrated infrequent alteration of validated lung cancer targets (including the absence of BRAF mutations in TTF1-negative LUAD), but identified novel potential targets for TTF1-negative LUAD, including KEAP1/Nrf2 and DNA repair pathways.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Negative Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 Expression Defines an Unfavorable Subgroup of Lung Adenocarcinomas.J Thorac Oncol. 2015 Oct;10(10):1444-50. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000626. J Thorac Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26200450
-
Integrated analysis of patients with KEAP1/NFE2L2/CUL3 mutations in lung adenocarcinomas.Cancer Med. 2021 Dec;10(23):8673-8692. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4338. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34617407 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 Loss induces characteristic patterns of gene expression in human tumors associated with NRF2 activation and attenuation of PI3K-AKT.J Thorac Oncol. 2014 Jun;9(6):794-804. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000173. J Thorac Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24828662 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of Nrf2 signal in non-small cell lung cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Feb 27;9:14. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0246-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26922479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the cell signaling pathway Keap1-Nrf2 as a therapeutic strategy for adenocarcinomas of the lung.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 Mar;23(3):241-250. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1559824. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30556750 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of thyroid transcription factor-1 with the efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2022 Aug;13(16):2309-2317. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14560. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35808895 Free PMC article.
-
IL6 Blockade Reprograms the Lung Tumor Microenvironment to Limit the Development and Progression of K-ras-Mutant Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 1;76(11):3189-99. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2840. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27197187 Free PMC article.
-
ZEB1 suppression sensitizes KRAS mutant cancers to MEK inhibition by an IL17RD-dependent mechanism.Sci Transl Med. 2019 Mar 13;11(483):eaaq1238. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaq1238. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30867319 Free PMC article.
-
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography correlates with tumor immunometabolic phenotypes in resected lung cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Aug;69(8):1519-1534. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02560-5. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32300858 Free PMC article.
-
SRGN-Triggered Aggressive and Immunosuppressive Phenotype in a Subset of TTF-1-Negative Lung Adenocarcinomas.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 Feb 7;114(2):290-301. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab183. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 34524427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bingle CD. Thyroid transcription factor-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:1471–3. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi T, Hosono Y, Yanagisawa K, Takahashi T. NKX2-1/TTF-1: an enigmatic oncogene that functions as a double-edged sword for cancer cell survival and progression. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:718–23. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi T, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kosaka T, Osada H, Yanagisawa K, et al. Expression profile-defined classification of lung adenocarcinoma shows close relationship with underlying major genetic changes and clinicopathologic behaviors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1679–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

