Role of the EHD2 unstructured loop in dimerization, protein binding and subcellular localization
- PMID: 25875965
- PMCID: PMC4398442
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123710
Role of the EHD2 unstructured loop in dimerization, protein binding and subcellular localization
Abstract
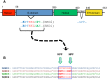
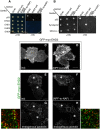
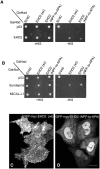
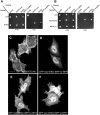
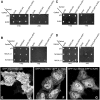
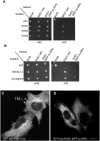
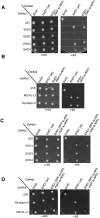
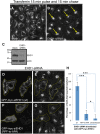
The C-terminal Eps 15 Homology Domain proteins (EHD1-4) play important roles in regulating endocytic trafficking. EHD2 is the only family member whose crystal structure has been solved, and it contains an unstructured loop consisting of two proline-phenylalanine (PF) motifs: KPFRKLNPF. In contrast, despite EHD2 having nearly 70% amino acid identity with its paralogs, EHD1, EHD3 and EHD4, the latter proteins contain a single KPF or RPF motif, but no NPF motif. In this study, we sought to define the precise role of each PF motif in EHD2's homo-dimerization, binding with the protein partners, and subcellular localization. To test the role of the NPF motif, we generated an EHD2 NPF-to-NAF mutant to mimic the homologous sequences of EHD1 and EHD3. We demonstrated that this mutant lost both its ability to dimerize and bind to Syndapin2. However, it continued to localize primarily to the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane. On the other hand, EHD2 NPF-to-APA mutants displayed normal dimerization and Syndapin2 binding, but exhibited markedly increased nuclear localization and reduced association with the plasma membrane. We then hypothesized that the single PF motif of EHD1 (that aligns with the KPF of EHD2) might be responsible for both binding and localization functions of EHD1. Indeed, the EHD1 RPF motif was required for dimerization, interaction with MICAL-L1 and Syndapin2, as well as localization to tubular recycling endosomes. Moreover, recycling assays demonstrated that EHD1 RPF-to-APA was incapable of supporting normal receptor recycling. Overall, our data suggest that the EHD2 NPF phenylalanine residue is crucial for EHD2 localization to the plasma membrane, whereas the proline residue is essential for EHD2 dimerization and binding. These studies support the recently proposed model in which the EHD2 N-terminal region may regulate the availability of the unstructured loop for interactions with neighboring EHD2 dimers, thus promoting oligomerization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in regulating EHD2 plasma membrane localization.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 10;8(9):e74519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074519. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040268 Free PMC article.
-
EHD3 Protein Is Required for Tubular Recycling Endosome Stabilization, and an Asparagine-Glutamic Acid Residue Pair within Its Eps15 Homology (EH) Domain Dictates Its Selective Binding to NPF Peptides.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 24;291(26):13465-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.716407. Epub 2016 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27189942 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal EH-domain-containing proteins: consensus for a role in endocytic trafficking, EH?J Cell Sci. 2005 Sep 15;118(Pt 18):4093-101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02595. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16155252
-
Scratching the surface: actin' and other roles for the C-terminal Eps15 homology domain protein, EHD2.Histol Histopathol. 2014 Mar;29(3):285-92. doi: 10.14670/HH-29.285. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Histol Histopathol. 2014. PMID: 24347515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EH domain-containing protein 2 (EHD2): Overview, biological function, and therapeutic potential.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Apr;42(3):e4016. doi: 10.1002/cbf.4016. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38613224 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic implication of histological features associated with EHD2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174737. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358874 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements for the Eps15 homology domain proteins EHD4 and EHD2 in the regulation of mammalian ciliogenesis.Traffic. 2022 Jul;23(7):360-373. doi: 10.1111/tra.12845. Epub 2022 May 17. Traffic. 2022. PMID: 35510564 Free PMC article.
-
Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 4 (EHD4) is required for Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 1 (EHD1)-mediated endosomal recruitment and fission.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 23;15(9):e0239657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239657. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32966336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kieken F, Jovic M, Naslavsky N, Caplan S, Sorgen PL (2007) EH domain of EHD1. J Biomol NMR 39: 323–329. - PubMed
-
- Kieken F, Sharma M, Jovic M, Giridharan SS, Naslavsky N, Caplan S, et al. (2010) Mechanism for the selective interaction of C-terminal Eps15 homology domain proteins with specific Asn-Pro-Phe-containing partners. The Journal of biological chemistry 285: 8687–8694. 10.1074/jbc.M109.045666 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

