Ryanodine receptor sensitization results in abnormal calcium signaling in airway smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 25874477
- PMCID: PMC4742950
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0386OC
Ryanodine receptor sensitization results in abnormal calcium signaling in airway smooth muscle cells
Abstract
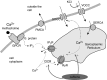
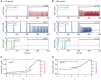
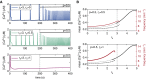
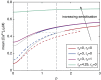
Intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics of airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) are believed to play a major role in airway hyperresponsiveness and remodeling in asthma. Prior studies have underscored a prominent role for inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptors in normal agonist-induced Ca(2+) oscillations, whereas ryanodine receptors (RyRs) appear to remain closed during such Ca(2+) oscillations, which mediate ASMC contraction. Nevertheless, RyRs have been hypothesized to play a role in hyperresponsive Ca(2+) signaling. This could be explained by RyRs being "sensitized" to open more frequently by certain compounds. We investigate the implications of RyR sensitization on Ca(2+) dynamics in ASMC using a combination of mathematical modeling and experiments with mouse precision-cut lung slices. Caffeine is used to increase the sensitivity of RyRs to cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)]SR). In ASMCs, high caffeine concentrations (>10 mM) induce a sustained elevation of [Ca(2+)]i. Our mathematical model accounts for this by the activation of store-operated Ca(2+) entry that results from a large increase in the RyR sensitivity to [Ca(2+)]SR and the associated Ca(2+) release, which leads to a reduction of [Ca(2+)]SR. Importantly, our model also predicts that: (1) moderate RyR sensitization induces slow Ca(2+) oscillations, a result experimentally confirmed with low concentrations of caffeine; and (2) high RyR sensitization suppresses fast, agonist-induced Ca(2+) oscillations by inducing substantial store-operated Ca(2+) entry and elevated [Ca(2+)]i. These results suggest that RyR sensitization could play a role in ASMC proliferation (by inducing slow Ca(2+) oscillations) and in airway hyperresponsiveness (by inducing greater mean [Ca(2+)]i for similar levels of contractile agonist).
Keywords: Ca2+ oscillations; asthma; hypersensitivity; mathematical modeling; precision-cut lung slice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The contribution of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and ryanodine receptors to agonist-induced Ca(2+) signaling of airway smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):L347-61. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90559.2008. Epub 2009 May 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19465516 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-13 enhanced Ca2+ oscillations in airway smooth muscle cells.Cytokine. 2012 Jan;57(1):19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.10.014. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22078634
-
Conformation of ryanodine receptor-2 gates store-operated calcium entry in rat pulmonary arterial myocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jul 1;111(1):94-104. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw067. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27013634 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcolemma agonist-induced interactions between InsP3 and ryanodine receptors in Ca2+ oscillations and waves in smooth muscle.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Oct;31(Pt 5):920-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0310920. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14505449 Review.
-
Microdomain elements of airway smooth muscle in calcium regulation and cell proliferation.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;69(2). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2018.2.01. Epub 2018 Jun 13. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29920471 Review.
Cited by
-
Caffeine modulates glucocorticoid-induced expression of CTGF in lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Respir Res. 2017 Mar 23;18(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0535-8. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 28330503 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue traction microscopy to quantify muscle contraction within precision-cut lung slices.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):L323-L330. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00297.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31774304 Free PMC article.
-
Inherent differences of small airway contraction and Ca2+ oscillations in airway smooth muscle cells between BALB/c and C57BL/6 mouse strains.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 5;11:1202573. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1202573. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37346175 Free PMC article.
-
Role of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in the modulation of airway smooth muscle tone and calcium handling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):L812-L821. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00064.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28336810 Free PMC article.
-
Airway smooth muscle function in asthma.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 5;13:993406. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.993406. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36277199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

