Modulation of CD44 Activity by A6-Peptide
- PMID: 25870596
- PMCID: PMC4378311
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00135
Modulation of CD44 Activity by A6-Peptide
Abstract
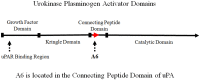
Hyaluronan (HA) is a non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed throughout the extracellular matrix that plays a major role in cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. CD44, a multifunctional cell surface glycoprotein, is a receptor for HA. In addition, CD44 is known to interact with other receptors and ligands, and to mediate a number of cellular functions as well as disease progression. Studies have shown that binding of HA to CD44 in cancer cells activates survival pathways resulting in cancer cell survival. This effect can be blocked by anti-CD44 monoclonal antibodies. A6 is a capped, eight l-amino acid peptide (Ac-KPSSPPEE-NH2) derived from the biologically active connecting peptide domain of the serine protease, human urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). A6 neither binds to the uPA receptor (uPAR) nor interferes with uPA/uPAR binding. A6 binds to CD44 resulting in the inhibition of migration, invasion, and metastasis of tumor cells, and the modulation of CD44-mediated cell signaling. A6 has been shown to have no dose-limiting toxicity in animal studies. A6 has demonstrated efficacy and an excellent safety profile in Phase 1a, 1b, and 2 clinical trials. In animal models, A6 has also exhibited promising results for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy and wet age-related macular degeneration through the reduction of retinal vascular permeability and inhibition of choroidal neovascularization, respectively. Recently, A6 has been shown to be directly cytotoxic for B-lymphocytes obtained from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia expressing the kinase, ZAP-70. This review will discuss the activity of A6, A6 modulation of HA and CD44, and a novel strategy for therapeutic intervention in disease.
Keywords: A6; CD44; CLL; HA; metastasis; ocular; recurrence; resistant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A6 peptide activates CD44 adhesive activity, induces FAK and MEK phosphorylation, and inhibits the migration and metastasis of CD44-expressing cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2072-82. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0351. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21885863
-
The urokinase/urokinase receptor system in retinal neovascularization: inhibition by A6 suggests a new therapeutic target.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Jun;44(6):2736-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-1160. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12766081
-
CD44 enhances invasion of basal-like breast cancer cells by upregulating serine protease and collagen-degrading enzymatic expression and activity.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 May 23;14(3):R84. doi: 10.1186/bcr3199. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22621373 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of tumor cell-induced extracellular matrix degradation--inhibition of cell-surface proteolytic activity might have a therapeutic effect on tumor cell invasion and metastasis].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):623-32. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808830 Review. Japanese.
-
Anticancer therapeutics: targeting macromolecules and nanocarriers to hyaluronan or CD44, a hyaluronan receptor.Mol Pharm. 2008 Jul-Aug;5(4):474-86. doi: 10.1021/mp800024g. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Mol Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18547053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30802498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications.Front Oncol. 2018 Feb 12;8:24. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00024. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix hyaluronan signals via its CD44 receptor in the increased responsiveness to mechanical stimulation.Neuroscience. 2016 Jun 2;324:390-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.03.032. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26996509 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronan as a therapeutic target in human diseases.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Feb 1;97:186-203. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.10.017. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26541745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Molecular Landscape in Mouse Models and Patients Reveals Conserved Inflammation Pathways in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Jan 2;65(1):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.1.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38175639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laufs S, Schumacher J, Allgayer H. Urokinase-receptor (u-PAR): an essential player in multiple games of cancer: a review on its role in tumor progression, invasion, metastasis, proliferation/dormancy, clinical outcome and minimal residual disease. Cell Cycle (2006) 5(16):1760–71.10.4161/cc.5.16.2994 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous