Looking beyond the induction of Th2 responses to explain immunomodulation by helminths
- PMID: 25869527
- PMCID: PMC4425638
- DOI: 10.1111/pim.12194
Looking beyond the induction of Th2 responses to explain immunomodulation by helminths
Abstract
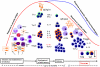
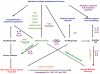
Although helminth infections are characteristically associated with Th2-mediated responses that include the production of the prototypical cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 by CD4(+) cells, the production of IgE, peripheral blood eosinophilia and mucus production in localized sites, these responses are largely attenuated when helminth infections become less acute. This modulation of the immune response that occurs with chronic helminth infection is often induced by molecules secreted by helminth parasites, by non-Th2 regulatory CD4(+) cells, and by nonclassical B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. This review will focus on those parasite- and host-mediated mechanisms underlying the modulated T-cell response that occurs as the default in chronic helminth infections.
Keywords: IL-10; IgE; IgG4; Th2 responses; alternatively activated macrophages; dendritic cells; helminths; immune modulation; innate lymphoid cells; regulatory B cells; regulatory T cells.
Published 2015. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helminth Infections: Recognition and Modulation of the Immune Response by Innate Immune Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 4;9:664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00664. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29670630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of specific and allergy-related immune responses by helminths.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:821578. doi: 10.1155/2011/821578. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22219659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural helper cells: a new player in the innate immune response against helminth infection.Adv Immunol. 2010;108:21-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380995-7.00002-1. Adv Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21056728
-
Alternatively activated macrophages in helminth infections.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):448-53. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Aug 16. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17702561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic helminth infections induce immunomodulation: consequences and mechanisms.Immunobiology. 2007;212(6):475-90. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.03.009. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544832 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Chikungunya Virus Infection Triggers a Diverse Range of T Helper Lymphocyte Profiles.Viruses. 2024 Aug 30;16(9):1387. doi: 10.3390/v16091387. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339863 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell molecular signature of pathogenic T helper subsets in type 2-associated disorders in humans.JCI Insight. 2024 Apr 8;9(7):e177720. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.177720. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38587077 Free PMC article.
-
Toxocara canis infection in multiple types of animals: ophthalmological and pathological observations.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Feb 23;17(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06070-y. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38395932 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Various Immune Cell Populations in Immune Response against Helminths.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 28;25(1):420. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010420. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the immunosuppressive environment induced by larval Echinococcus granulosus during chronic experimental infection.Infect Immun. 2024 Feb 13;92(2):e0027623. doi: 10.1128/iai.00276-23. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38174942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen JE, Maizels RM. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:375–388. - PubMed
-
- Harnett W, Harnett MM. Lymphocyte hyporesponsiveness during filarial nematode infection. Parasite Immunol. 2008;30:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Wammes LJ, Hamid F, Wiria AE, et al. Regulatory T cells in human geohelminth infection suppress immune responses to BCG and Plasmodium falciparum. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:437–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

