Identification of a Non-Gatekeeper Hot Spot for Drug-Resistant Mutations in mTOR Kinase
- PMID: 25865887
- PMCID: PMC4761412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.040
Identification of a Non-Gatekeeper Hot Spot for Drug-Resistant Mutations in mTOR Kinase
Abstract
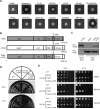
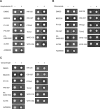
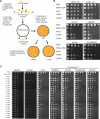
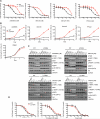
Protein kinases are therapeutic targets for human cancer. However, "gatekeeper" mutations in tyrosine kinases cause acquired clinical resistance, limiting long-term treatment benefits. mTOR is a key cancer driver and drug target. Numerous small-molecule mTOR kinase inhibitors have been developed, with some already in human clinical trials. Given our clinical experience with targeted therapeutics, acquired drug resistance in mTOR is thought likely, but not yet documented. Herein, we describe identification of a hot spot (L2185) for drug-resistant mutations, which is distinct from the gatekeeper site, and a chemical scaffold refractory to drug-resistant mutations. We also provide new insights into mTOR kinase structure and function. The hot spot mutations are potentially useful as surrogate biomarkers for acquired drug resistance in ongoing clinical trials and future treatments and for the design of the next generation of mTOR-targeted drugs. Our study provides a foundation for further research into mTOR kinase function and targeting.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a new-generation mTOR inhibitor.Nature. 2016 Jun 9;534(7606):272-6. doi: 10.1038/nature17963. Epub 2016 May 18. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27279227 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to dual blockade of the kinases PI3K and mTOR in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer models results in combined sensitivity to inhibition of the receptor tyrosine kinase EGFR.Sci Signal. 2014 Nov 11;7(351):ra107. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005516. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 25389372
-
MTOR mutations in the crosshairs of targeted therapy.Cancer Discov. 2014 May;4(5):513-5. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0332. Cancer Discov. 2014. PMID: 24795009
-
Therapeutic resistance resulting from mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Nov;226(11):2762-81. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22647. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21302297 Review.
-
Preclinical rationale for PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors as therapy for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2013 Jul;14(4):322-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2012.12.001. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23332287 Review.
Cited by
-
PP2AC Level Determines Differential Programming of p38-TSC-mTOR Signaling and Therapeutic Response to p38-Targeted Therapy in Colorectal Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 19;2(12):1944-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.031. eCollection 2015 Dec. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26844273 Free PMC article.
-
How to tackle antimalarial resistance?EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Feb;9(2):133-134. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201607295. EMBO Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28028013 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Extremely Damaging IRAK4 Variants and Their Potential Implications for IRAK4 Inhibitor Efficacy.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 26;13(12):1648. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121648. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138875 Free PMC article.
-
SOD1 Phosphorylation by mTORC1 Couples Nutrient Sensing and Redox Regulation.Mol Cell. 2018 May 3;70(3):502-515.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.03.029. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29727620 Free PMC article.
-
A system to identify inhibitors of mTOR signaling using high-resolution growth analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Geroscience. 2017 Aug;39(4):419-428. doi: 10.1007/s11357-017-9988-4. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Geroscience. 2017. PMID: 28707282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alarcon CM, Cardenas ME, Heitman J. Mammalian RAFT1 kinase domain provides rapamycin-sensitive TOR function in yeast. Genes & development. 1996;10:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Azam M, Latek RR, Daley GQ. Mechanisms of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell. 2003;112:831–843. - PubMed
-
- Bell DW, Gore I, Okimoto RA, Godin-Heymann N, Sordella R, Mulloy R, Sharma SV, Brannigan BW, Mohapatra G, Settleman J, et al. Inherited susceptibility to lung cancer may be associated with the T790M drug resistance mutation in EGFR. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1315–1316. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti M-A, Houghton PJ. The tor pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:335–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

