Silencing β3 Integrin by Targeted ECO/siRNA Nanoparticles Inhibits EMT and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 25858145
- PMCID: PMC4452414
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3485
Silencing β3 Integrin by Targeted ECO/siRNA Nanoparticles Inhibits EMT and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
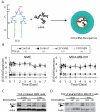
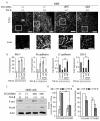
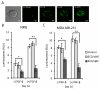
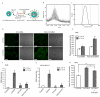
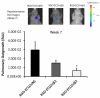
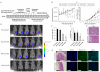
Metastatic breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive subcategory of breast cancer and currently lacks well-defined molecular targets for effective targeted therapies. Disease relapse, metastasis, and drug resistance render standard chemotherapy ineffective in the treatment of TNBC. Because previous studies coupled β3 integrin (ITGB3) to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis, we exploited β3 integrin as a therapeutic target to treat TNBC by delivering β3 integrin siRNA via lipid ECO-based nanoparticles (ECO/siβ3). Treatment of TNBC cells with ECO/siβ3 was sufficient to effectively silence β3 integrin expression, attenuate TGFβ-mediated EMT and invasion, restore TGFβ-mediated cytostasis, and inhibit three-dimensional organoid growth. Modification of ECO/siβ3 nanoparticles with an RGD peptide via a PEG spacer enhanced siRNA uptake by post-EMT cells. Intravenous injections of RGD-targeted ECO/siβ3 nanoparticles in vivo alleviated primary tumor burden and, more importantly, significantly inhibited metastasis. In the span of 16 weeks of the experiments and observations, including primary tumor resection at week 9 and release from the treatment for 4 weeks, the mice bearing orthotopic, TGFβ-prestimulated MDA-MB-231 tumors that were treated with RGD-targeted ECO/siβ3 nanoparticles were free of metastases and relapse, in comparison with untreated mice. Collectively, these results highlight ECO/siβ3 nanoparticles as a promising therapeutic regimen to combat TNBC.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic Delivery of Tumor-Targeting siRNA Nanoparticles against an Oncogenic LncRNA Facilitates Effective Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy.Bioconjug Chem. 2019 Mar 20;30(3):907-919. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00028. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Bioconjug Chem. 2019. PMID: 30739442 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a natural small-molecule compound that suppresses tumor EMT, stemness and metastasis by inhibiting TGFβ/BMP signaling in triple-negative breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 21;38(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1130-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30898152 Free PMC article.
-
Pristimerin exerts antitumor activity against MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells by reversing of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via downregulation of integrin β3.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6 Suppl 1):S84-S92. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.07.004. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 35652598 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Delivery of TWIST Small Interfering RNA and Anticancer Drugs: A Therapeutic Approach for Combating Cancer.Enzymes. 2018;44:83-101. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2018.08.004. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Enzymes. 2018. PMID: 30360816 Review.
-
Nanosoldiers: A promising strategy to combat triple negative breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:319-341. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.122. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30529766 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances and Mechanism of Nanomaterials Promoting Tumor Metastasis.Environ Health (Wash). 2023 Nov 9;1(6):367-382. doi: 10.1021/envhealth.3c00132. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. Environ Health (Wash). 2023. PMID: 39474052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated targeted drug delivery for breast cancer treatment.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019 Apr;1871(2):419-433. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31034927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling metastatic cancer: the role of phytochemicals in cell signaling.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 May;145(5):1087-1109. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02892-5. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30903319 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Use of Nanoparticle Delivery to Overcome Resistance in Breast Cancers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1347:163-181. doi: 10.1007/5584_2021_648. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34287795
-
Silencing the roadblocks to effective triple-negative breast cancer treatments by siRNA nanoparticles.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017 Apr;24(4):R81-R97. doi: 10.1530/ERC-16-0482. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28148541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(4):220–41. - PubMed
-
- O’Toole SA, Beith JM, Millar EK, West R, McLean A, Cazet A, et al. Therapeutic targets in triple negative breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(6):530–42. - PubMed
-
- Metzger-Filho O, Tutt A, de Azambuja E, Saini KS, Viale G, Loi S, et al. Dissecting the heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(15):1879–87. - PubMed
-
- Turner N, Moretti E, Siclari O, Migliaccio I, Santarpia L, D’Incalci M, et al. Targeting triple negative breast cancer: is p53 the answer? Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39(5):541–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

