MicroRNA-199a-3p suppresses glioma cell proliferation by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 25854175
- PMCID: PMC4644202
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-015-3409-z
MicroRNA-199a-3p suppresses glioma cell proliferation by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
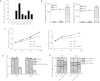
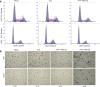
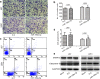
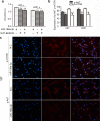
Glioma has been investigated for decades, but the prognosis remains poor because of rapid proliferation, its aggressive potential, and its resistance to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is highly expressed and regulates cellular proliferation and cell growth. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene transcription and translation via up-regulating or down-regulating the levels of miRNAs. This study was conducted to explore the molecular functions of miR-199a-3p in glioma. We detected the expression of miR-199a-3p in glioma samples by quantitative PCR (qPCR). Then, we transfected the U87 and U251 cell lines with miR-199a-3p. Cellular proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis were assessed to explain the function of miR-199a-3p. PCR confirmed that the expression of miR-199a-3p was lower in glioma samples combined with normal brain tissues. The over-expression of miR-199a-3p might target mTOR and restrained cellular growth and proliferation but not invasive and apoptosis capability. Results indicated that cellular proliferation was inhibited to regulate the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by elevating levels of miR-199a-3p. MiR-199a-3p in glioma cell lines has effects similar to the tumor suppressor gene on cellular proliferation via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Keywords: Glioma; Proliferation; mTOR; miR-199a-3p.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-199a-3p regulates endometrial cancer cell proliferation by targeting mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR).Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2013 Sep;23(7):1191-7. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0b013e31829ea779. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23851675
-
MicroRNA-199a-3p is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and modulates cell proliferation.Genet Mol Res. 2013 Aug 20;12(3):3038-47. doi: 10.4238/2013.August.20.5. Genet Mol Res. 2013. PMID: 24065659
-
MiR-199a/b-3p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation via down-regulating PAK4/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jan 5;18(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3949-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29304764 Free PMC article.
-
miR-199a: A Tumor Suppressor with Noncoding RNA Network and Therapeutic Candidate in Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 31;23(15):8518. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158518. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of microRNA-199a Regulation in Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Dec 10;11:10327-10335. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S231971. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31849522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum microRNA-199a/b-3p as a predictive biomarker for treatment response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 May 4;9:2667-74. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S98408. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27226729 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway and expression of MDR1.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33621-33630. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16834. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422725 Free PMC article.
-
miR-199a/b-3p inhibits HCC cell proliferation and invasion through a novel compensatory signaling pathway DJ-1\Ras\PI3K/AKT.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48760-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38168113 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA expression profile of mouse Müller glia in vivo and in vitro.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 14;6:35423. doi: 10.1038/srep35423. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27739496 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking lncRNA MALAT1/miR-199a/ZHX1 Axis Inhibits Glioblastoma Proliferation and Progression.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Dec 6;18:388-399. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31648104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maira SM, Stauffer F, Brueggen J, Furet P, Schnell C, Fritsch C, et al. Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:1851–1863. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

