Falls among hemodialysis patients: potential opportunities for prevention?
- PMID: 25852886
- PMCID: PMC4377754
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfu034
Falls among hemodialysis patients: potential opportunities for prevention?
Abstract
Background: Falls among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (HD) have significant consequences for quality of life and functional independence, morbidity, healthcare utilization and even mortality, but studies on the etiology of falls within large HD cohorts are limited.
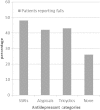
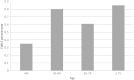
Methods: Falls during the past 12 months were ascertained for a prevalent multi-center HD cohort (n = 762) aged 20-92 years, and associations with demographic and treatment characteristics, comorbidities, cognitive function, prescribed medications, balance tests, frailty and depressive symptoms were assessed.
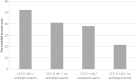
Results: Falls were sustained by 28.4% of participants. In multivariable-adjusted analyses, participants classified as frail were over two times more likely to report falls [odds ratio (OR): 2.39, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.22-4.71, P = 0.01], and participants with a CES-D score 18+ and/or prescribed antidepressants were over 80% more likely to be fallers (OR: 1.83, 95% CI: 1.23-2.74, P = 0.003) than were participants with a CES-D score <18 and no prescribed antidepressants.
Conclusions: Frailty and depressed mood, factors that are potentially modifiable, are prominently associated with falls.
Keywords: USRDS; depression; falls; frailty; hemodialysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Motor Performance and Physical Activity as Predictors of Prospective Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults by Frailty Level: Application of Wearable Technology.Gerontology. 2016;62(6):654-664. doi: 10.1159/000445889. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Gerontology. 2016. PMID: 27160666 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional status in relation to balance and falls in the elderly: a preliminary look at serum folate.Ann Nutr Metab. 2009;54(1):59-66. doi: 10.1159/000207356. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Ann Nutr Metab. 2009. PMID: 19270446
-
Association of Clinical Frailty Scores With Hospital Readmission for Falls After Index Admission for Trauma-Related Injury.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Oct 2;2(10):e1912409. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12409. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31577357 Free PMC article.
-
Frailty and risk of falls, fracture, and mortality in older women: the study of osteoporotic fractures.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007 Jul;62(7):744-51. doi: 10.1093/gerona/62.7.744. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17634322
-
Interventions to Prevent Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Apr. Report No.: 17-05232-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Apr. Report No.: 17-05232-EF-1. PMID: 30234932 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Interventions to reduce falls among dialysis patients: a systematic review.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Dec 21;24(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03408-7. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 38129770 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of falls and fall-related injuries among middle-aged adults with kidney disease.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Sep;51(9):1613-1621. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02148-8. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31165398
-
Use of frailty assessment instruments in nephrology populations: a scoping review.BMC Geriatr. 2023 Jul 21;23(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04101-y. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37479978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relative importance of frailty, physical and cardiovascular function as exercise-modifiable predictors of falls in haemodialysis patients: a prospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Mar 14;21(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01759-z. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32169050 Free PMC article.
-
The utility of FRAX® in predicting bone fractures in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis: a two-year prospective multicenter cohort study.Osteoporos Int. 2018 May;29(5):1105-1115. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4406-z. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29411069
References
-
- Roberts RG, Kenny RA, Brierley EJ. Are elderly haemodialysis patients at risk of falls and postural hypotension? Int Urol Nephrol. 2003;35:415–421. - PubMed
-
- Desmet C, Beguin C, Swine C, et al. the Universitė Catholique de Louvain Collaborative Group. Falls in hemodialysis patients: prospective study of incidence, risk factors, and complications. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45:148–153. - PubMed
-
- Cook WL, Jassal SV. Prevalence of falls among seniors maintained on hemodialysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2005;37:649–652. - PubMed
-
- Cook WL, Tomlinson G, Donaldson M, et al. Falls and fall-related injuries in older dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Tomlinson G, Naglie G, et al. Geriatric comorbidities, such as falls, confer an independent mortality risk to elderly dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:1396–1400. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

