Inherent transcriptional signatures of NK cells are associated with response to IFNα + rivabirin therapy in patients with Hepatitis C Virus
- PMID: 25849716
- PMCID: PMC4353456
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-015-0428-x
Inherent transcriptional signatures of NK cells are associated with response to IFNα + rivabirin therapy in patients with Hepatitis C Virus
Abstract
Background: Differences in the expression of Natural Killer cell receptors have been reported to reflect divergent clinical courses in patients with chronic infections or tumors. However, extensive molecular characterization at the transcriptional level to support this view is lacking. The aim of this work was to characterize baseline differences in purified NK cell transcriptional activity stratified by response to treatment with PEG-IFNα/RBV in patients chronically infected with HCV.
Methods: To this end we here studied by flow cytometer and gene expression profile, phenotypic and transcriptional characteristics of purified NK cells in patients chronically infected with HCV genotype-1 virus who were subsequently treated with PEG-IFNα/RBV. Results were further correlated with divergent clinical response obtained after treatment.
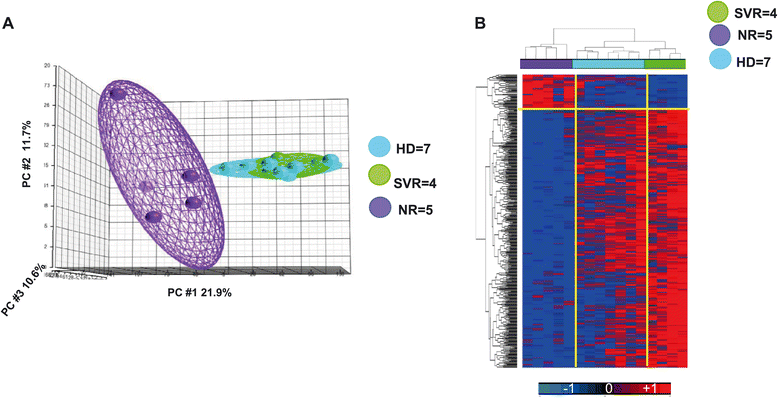
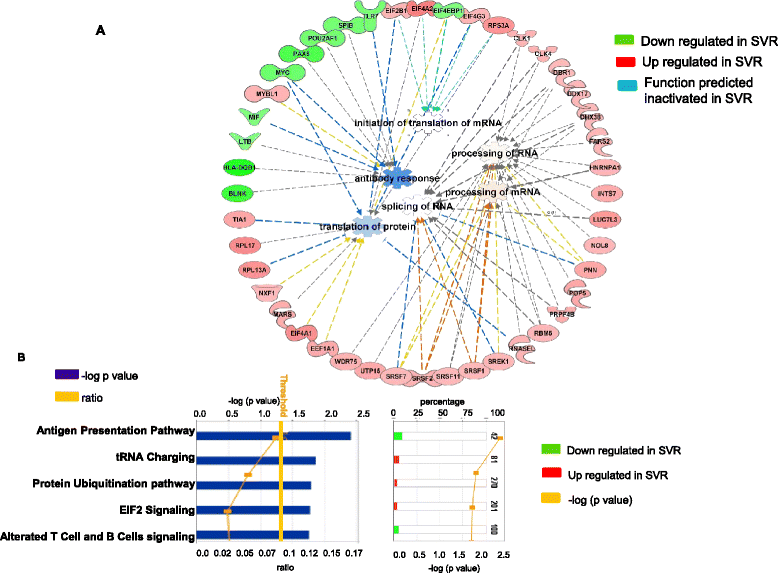
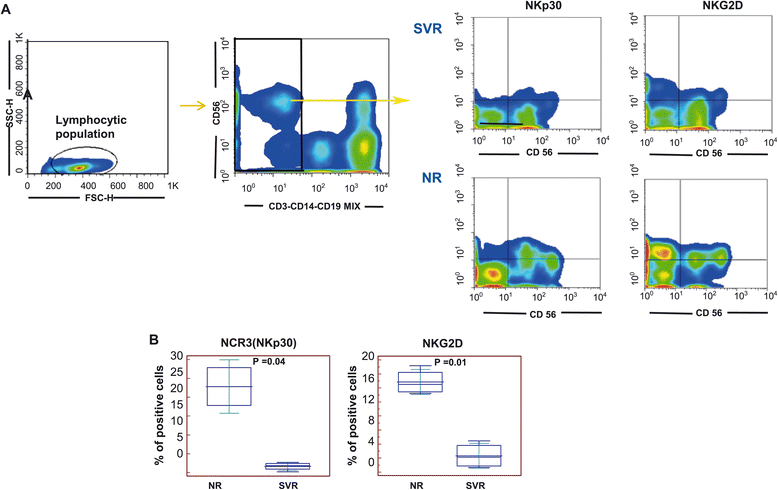
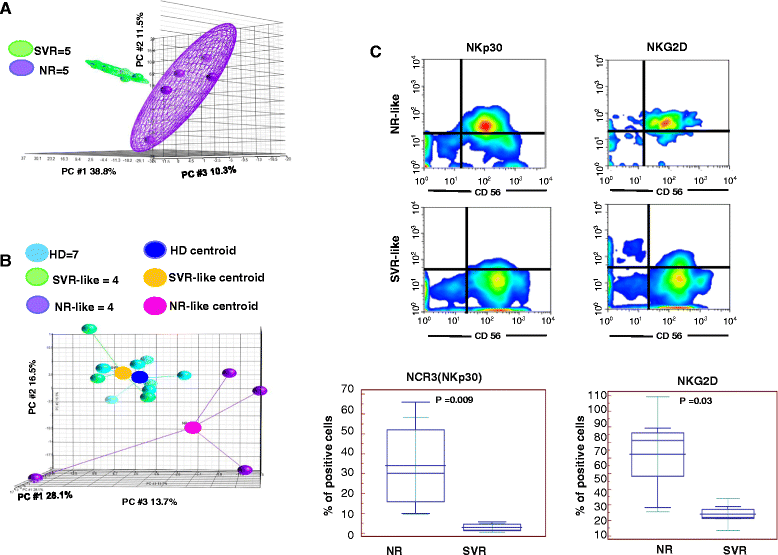
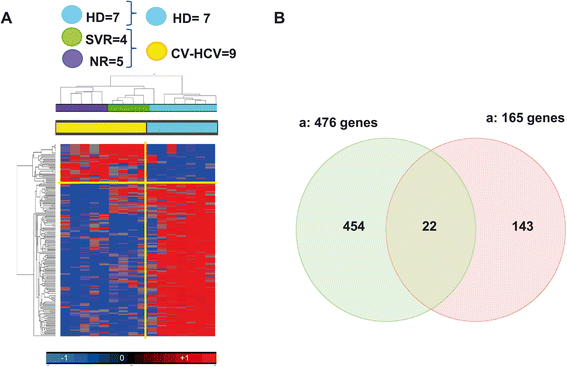
Results: The pre-treatment transcriptional patterns of purified NK cells from patients subsequently undergoing a sustained virologic response (SVR) clearly segregated from those of non-responder (NR) patients. A set of 476 transcripts, including molecules involved in RNA processing, ubiquitination pathways as well as HLA class II signalling were differently expressed among divergent patients. In addition, treatment outcome was associated with differences in surface expression of NKp30 and NKG2D. A complex relationship was observed that suggested for extensive post-transcriptional editing. Only a small number of the NK cell transcripts identified were correlated with chronic HCV infection/replication indicating that inherent transcriptional activity prevails over environment effects such as viral infection.
Conclusions: Collectively, inherent/genetic modulation of NK cell transcription is involved in setting the path to divergent treatment outcomes and could become useful to therapeutic advantage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-λ3 polymorphisms in pegylated-interferon-α plus ribavirin therapy for genotype-2 chronic hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 7;21(13):3904-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3904. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25852275 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-alpha-induced TRAIL on natural killer cells is associated with control of hepatitis C virus infection.Gastroenterology. 2010 May;138(5):1885-97. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.01.051. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20334827
-
Association of NKG2A with treatment for chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Aug;161(2):306-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04169.x. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20550548 Free PMC article.
-
IL28B rs12980275 variant as a predictor of sustained virologic response to pegylated-interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct;39(5):576-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25769643 Review.
-
Vitamin D level and sustained virologic response to interferon-based antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2014 Dec;61(6):1247-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25135863 Review.
Cited by
-
Melanoma: From Incurable Beast to a Curable Bet. The Success of Immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2015 Jul 13;5:152. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00152. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26217587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of the HIV-1 DNA Reservoir Is Associated In Vivo and In Vitro with NKp46/NKp30 (CD335 CD337) Inducibility and Interferon Gamma Production by Transcriptionally Unique NK Cells.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e00647-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00647-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28956765 Free PMC article.
-
An Historical Overview: The Discovery of How NK Cells Can Kill Enemies, Recruit Defense Troops, and More.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 19;10:1415. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01415. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31316503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell marker gene-based model shows good predictive ability in prognosis and response to immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 May 5;13(1):7294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34602-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37147523 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation of the Natural Killer Cell Phenotype and Response during HCV Infection.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 6;9(4):1030. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041030. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32268490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

