Oral administration of non-absorbable delayed release 6-mercaptopurine is locally active in the gut, exerts a systemic immune effect and alleviates Crohn's disease with low rate of side effects: results of double blind Phase II clinical trial
- PMID: 25846055
- PMCID: PMC4516452
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12640
Oral administration of non-absorbable delayed release 6-mercaptopurine is locally active in the gut, exerts a systemic immune effect and alleviates Crohn's disease with low rate of side effects: results of double blind Phase II clinical trial
Abstract
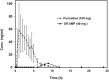
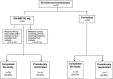
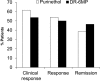
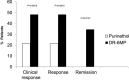
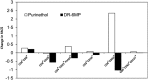
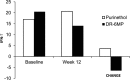
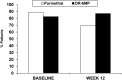
Therapy for Crohn's disease (CD) with thiopurines is limited by systemic side effects. A novel formulation of fixed-dose, delayed-release 6-mercaptopurine (DR-6MP) was developed, with local effect on the gut immune system and minimal absorption. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of DR-6MP in patients with moderately severe CD compared to systemically delivered 6-mercaptopurine (Purinethol). Seventy CD patients were enrolled into a 12-week, double-blind controlled trial. The primary end-point was the percentage of subjects with clinical remission [Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI) < 150] or clinical response (100-point CDAI reduction). Twenty-six (56·5%) and 13 (54·2%) subjects from the DR-6MP and Purinethol cohorts, respectively, completed the study. DR-6MP had similar efficacy to Purinethol following 12 weeks of treatment. However, the time to maximal clinical response was 8 weeks for DR-6MP versus 12 weeks for Purinethol. A higher proportion of patients on DR-6MP showed clinical remission at week 8. A greater improvement in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ) score was noted in the DR-6MP group. DR-6MP led to a decrease of CD62(+) expression on T cells, implying a reduction of lymphocyte adhesion to site of inflammation. DR-6MP was safer than Purinethol, with significantly fewer adverse events (AEs). There was no evidence of drug-induced leucopenia in the DR-6MP group; the proportion of subjects who developed hepatotoxicity was lower for the DR-6MP. Non-absorbable DR-6MP is safe and biologically active in the gut. It is clinically effective, exerting a systemic immune response with low systemic bioavailability and a low incidence of side effects.
Keywords: 6-mercaptopurine; Crohn's disease; gut immune system; oral therapy.
© 2015 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimum duration of treatment with 6-mercaptopurine for Crohn's disease.Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Nov;94(11):3254-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01532.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10566725
-
Azathioprine: state of the art in inflammatory bowel disease.Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1998;225:92-9. doi: 10.1080/003655298750027290. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9515759 Review.
-
Malignant neoplasms subsequent to treatment of inflammatory bowel disease with 6-mercaptopurine.Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Nov;94(11):3248-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01530.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10566724
-
Rifaximin-extended intestinal release induces remission in patients with moderately active Crohn's disease.Gastroenterology. 2012 Mar;142(3):473-481.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.032. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22155172 Clinical Trial.
-
Thiopurine-induced pancreatitis in inflammatory bowel diseases.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Apr;9(4):399-403. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2015.992879. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25494551 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Dose Colchicine Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury: A Novel Method for Alleviating Systemic Inflammation.Inflammation. 2023 Jun;46(3):963-974. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01783-9. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36656466
-
A digital health platform for assisting the diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19 progression: An adjuvant approach for augmenting the antiviral response and mitigating the immune-mediated target organ damage.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112228. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112228. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34649354 Free PMC article.
-
Azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine for induction of remission in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 26;10(10):CD000545. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000545.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27783843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orally administered anti-eotaxin-1 monoclonal antibody is biologically active in the gut and alleviates immune-mediated hepatitis: A novel anti-inflammatory personalized therapeutic approach.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:20587384211021215. doi: 10.1177/20587384211021215. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34275345 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding and managing pediatric inflammatory bowel disease.F1000Res. 2019 Dec 13;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-2097. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.19609.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31885858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Waters OR, Lawrance IC. Understanding the use of immunosuppressive agents in the clinical management of IBD. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:1364–71. - PubMed
-
- Bokkerink JP, Stet EH, De Abreu RA. 6-Mercaptopurine: cytotoxicity and biochemical pharmacology in human malignant T-lymphoblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993;45:1455–63. - PubMed
-
- Ebbesen MS, Nersting J, Jacobsen JH, et al. Incorporation of 6-thioguanine nucleotides into DNA during maintenance therapy of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia-the influence of thiopurine methyltransferase genotypes. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53:670–4. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Horin S, Goldstein I, Fudim E, et al. Early preservation of effector functions followed by eventual T cell memory depletion: a model for the delayed onset of the effect of thiopurines. Gut. 2009;58:396–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

