IFI35, mir-99a and HCV genotype to predict sustained virological response to pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 25844942
- PMCID: PMC4386819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121395
IFI35, mir-99a and HCV genotype to predict sustained virological response to pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
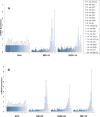
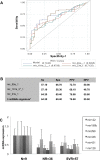
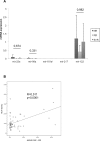
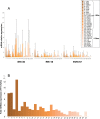
Although, the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) greatly improved with the use of direct antiviral agents, pegylated-interferon (PEG-IFN) plus ribavirin remains an option for many patients, worldwide. The intra-hepatic level of expression of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs) and the rs12979860 CC genotype located within IFNL3 have been associated with sustained virological response (SVR), in patients with CHC. The aim of the study was to identify micro-RNAs associated with SVR and to build an accurate signature to predict SVR. Pre-treatment liver biopsies from 111 patients, treated with PEG-IFN plus ribavirin, were studied. Fifty-seven patients had SVR, 36 non-response (NR) and 18 relapse (RR). The expression of 851 human miRNAs and 30 selected mRNAs, including ISGs, was assessed by RT-qPCR. In the first group of patients (screen), 20 miRNAs out of the 851 studied were deregulated between NRs and SVRs. From the 4 miRNAs validated (mir-23a, mir-181a*, mir-217 and mir-99a), in the second group of patients (validation), 3 (mir-23a, mir-181a* and mir-99a) were down-regulated in NRs as compared to SVRs. The ISGs, studied, were accumulated in SVRs and IFNL3 rs12979860 CT/TT carriers compared respectively to NRs and CC carriers. Combining, clinical data together with the expression of selected genes and micro-RNAs, we identified a signature (IFI35, mir-99a and HCV genotype) to predict SVR (AUC:0.876) with a positive predictive value of 86.54% with high sensibility (80%) and specificity (80.4%). This signature may help to characterize patients with low chance to respond to PEG-IFN/ribavirin and to elucidate mechanisms of NR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of microRNA 122 expression in IFNL3 CT/TT carriers and during progression of fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):6394-402. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00016-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24672032 Free PMC article.
-
Liver gene expression signature to predict response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Gut. 2008 Apr;57(4):516-24. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.128611. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Gut. 2008. PMID: 17895355
-
Serum interferon-related microRNAs as biomarkers to predict the response to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 19;10(3):e0120794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120794. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25790297 Free PMC article.
-
[The value of genetics in the era of hepatitis C triple therapy].Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Aug-Sep;37(7):427-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24948442 Review. Spanish.
-
Role of Interferons in Chronic Hepatitis C Infection.Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(7):844-850. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160201112632. Curr Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 26844564 Review.
Cited by
-
Pretreatment Predictors of Response to PegIFN-RBV Therapy in Egyptian Patients with HCV Genotype 4.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0153895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153895. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100663 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-based diagnostic tools for advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B and C.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:34935. doi: 10.1038/srep34935. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731343 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential mRNA panels for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (COVID-19) diagnosis and treatment using microarray dataset and bioinformatics methods.3 Biotech. 2020 Oct;10(10):422. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02406-y. Epub 2020 Sep 11. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 33251083 Free PMC article.
-
IFP35 Is a Relevant Factor in Innate Immunity, Multiple Sclerosis, and Other Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Review.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 14;10(12):1325. doi: 10.3390/biology10121325. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marcellin P, Asselah T, Boyer N. Fibrosis and disease progression in hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002; 36: S47–56. - PubMed
-
- Seeff LB. Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002; 36: S35–46. - PubMed
-
- Estrabaud E, Vidaud M, Marcellin P, Asselah T. Genomics and HCV infection: progression of fibrosis and treatment response. J Hepatol. 2012; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

