Therapeutic effects of adropin on glucose tolerance and substrate utilization in diet-induced obese mice with insulin resistance
- PMID: 25830094
- PMCID: PMC4354928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.01.005
Therapeutic effects of adropin on glucose tolerance and substrate utilization in diet-induced obese mice with insulin resistance
Abstract
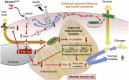
Objective: The peptide hormone adropin regulates fuel selection preferences in skeletal muscle under fed and fasted conditions. Here, we investigated whether adropin treatment can ameliorate the dysregulation of fuel substrate metabolism, and improve aspects of glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obesity (DIO) with insulin resistance.
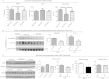
Methods: DIO C57BL/6 mice maintained on a 60% kcal fat diet received five intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of the bioactive peptide adropin(34-76) (450 nmol/kg/i.p.). Following treatment, glucose tolerance and whole body insulin sensitivity were assessed and indirect calorimetry was employed to analyze whole body substrate oxidation preferences. Biochemical assays performed in skeletal muscle samples analyzed insulin signaling action and substrate oxidation.
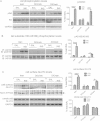
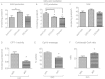
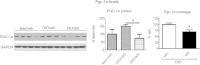
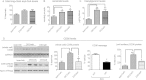
Results: Adropin treatment improved glucose tolerance, enhanced insulin action and augmented metabolic flexibility towards glucose utilization. In muscle, adropin treatment increased insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation and cell-surface expression of GLUT4 suggesting sensitization of insulin signaling pathways. Reduced incomplete fatty acid oxidation and increased CoA/acetyl-CoA ratio suggested improved mitochondrial function. The underlying mechanisms appear to involve suppressions of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1B (CPT-1B) and CD36, two key enzymes in fatty acid utilization. Adropin treatment activated pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), a rate-limiting enzyme in glucose oxidation, and downregulated PDH kinase-4 (PDK-4) that inhibits PDH. Along with these changes, adropin treatment downregulated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1α that regulates expression of Cpt1b, Cd36 and Pdk4.
Conclusions: Adropin treatment of DIO mice enhances glucose tolerance, ameliorates insulin resistance and promotes preferential use of carbohydrate over fat in fuel selection. Skeletal muscle is a key organ in mediating adropin's whole-body effects, sensitizing insulin signaling pathways and altering fuel selection preference to favor glucose while suppressing fat oxidation.
Keywords: Adropin; Fatty acid metabolism; Glucose metabolism; Insulin action; Metabolic flexibility; Mitochondrial function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of substrate oxidation preferences in muscle by the peptide hormone adropin.Diabetes. 2014 Oct;63(10):3242-52. doi: 10.2337/db14-0388. Epub 2014 May 21. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24848071 Free PMC article.
-
The peptide hormone adropin regulates signal transduction pathways controlling hepatic glucose metabolism in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity.J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 6;294(36):13366-13377. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008967. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31324719 Free PMC article.
-
Adropin regulates cardiac energy metabolism and improves cardiac function and efficiency.Metabolism. 2019 Sep;98:37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Metabolism. 2019. PMID: 31202835
-
Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:124-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24362249 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases in the prevention of hyperglycaemia.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002 Jul;2(2):151-65. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2002. PMID: 12476789 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling muscle transcriptome in mice exposed to microgravity using gene set enrichment analysis.NPJ Microgravity. 2024 Oct 4;10(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41526-024-00434-z. NPJ Microgravity. 2024. PMID: 39367013 Free PMC article.
-
Adropin, a novel hepatokine: localization and expression during postnatal development and its impact on testicular functions of pre-pubertal mice.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Feb;395(2):171-187. doi: 10.1007/s00441-023-03852-9. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 38087073
-
The Comparison of Irisin, Subfatin, and Adropin in Normal-Weight and Obese Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients.Iran J Med Sci. 2024 Jun 1;49(6):350-358. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2023.99130.3117. eCollection 2024 Jun. Iran J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38952638 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic PTEN Signaling Regulates Systemic Metabolic Homeostasis through Hepatokines-Mediated Liver-to-Peripheral Organs Crosstalk.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 2;23(7):3959. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073959. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409319 Free PMC article.
-
Low plasma adropin concentrations increase risks of weight gain and metabolic dysregulation in response to a high-sugar diet in male nonhuman primates.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 21;294(25):9706-9719. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007528. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30988006 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

