β-Cell Sensitivity to GLP-1 in Healthy Humans Is Variable and Proportional to Insulin Sensitivity
- PMID: 25825945
- PMCID: PMC4454808
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2014-4009
β-Cell Sensitivity to GLP-1 in Healthy Humans Is Variable and Proportional to Insulin Sensitivity
Abstract
Context: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an insulinotropic factor made in the gastrointestinal tract that is essential for normal glucose tolerance. Infusion of GLP-1 increases insulin secretion in both diabetic and nondiabetic humans. However, the degree to which people vary in their β-cell sensitivity to GLP-1 and the factors contributing to this variability have not been reported.
Objective: The objective was to measure the sensitivity of insulin secretion to GLP-1 in cohorts of lean and obese subjects across a broad range of insulin sensitivity.
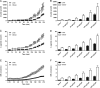
Methods: Insulin secretion was measured during clamped hyperglycemia (7.2 mmol/L) and graded GLP-1 infusion in young, healthy subjects, and GLP-1 sensitivity was computed from the insulin secretion rate (ISR) during progressive increases in plasma GLP-1.
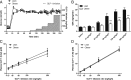
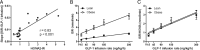
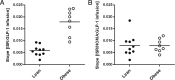
Results: All subjects had fasting glucose values <5.2 mm. The obese subjects were insulin resistant compared to the lean group (homeostasis model of assessment 2 for insulin resistance: obese, 2.6 ± 0.5; lean, 0.8 ± 0.1; P < .001). ISR increased linearly in both cohorts with escalating doses of GLP-1, but the slope of ISR in response to GLP-1 was greater in the obese than in the lean subjects (obese, 0.17 ± 0.03 nmol/min/pm; lean, 0.05 ± 0.01 nmol/min/pm; P < .001). There was a significant association of β-cell GLP-1 sensitivity and insulin resistance (r = 0.83; P < .001), and after correction for homeostasis model of assessment 2 for insulin resistance, the slopes of ISR vs GLP-1 concentration did not differ in the two cohorts (obese, 0.08 ± 0.01; lean, 0.08 ± 0.01; P = .98). However, within the entire study group, β-cell GLP-1 sensitivity corrected for insulin resistance varied nearly 10-fold.
Conclusions: Insulin secretion in response to GLP-1 is proportional to insulin resistance in healthy subjects. However, there is considerable variability in the sensitivity of the β-cell to GLP-1 that is independent of insulin sensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin sensitivity and secretion changes after gastric bypass in normotolerant and diabetic obese subjects.Ann Surg. 2013 Mar;257(3):462-8. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318269cf5c. Ann Surg. 2013. PMID: 23388352
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 augments insulin-mediated glucose uptake in the obese state.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Aug;87(8):3768-73. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.8.8743. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12161508 Clinical Trial.
-
Incretin secretion in relation to meal size and body weight in healthy subjects and people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Jun;88(6):2706-13. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021873. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12788877
-
Mechanisms of improved glycaemic control after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5057. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872541 Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1-potentiated insulin secretion and proliferation of pancreatic β-cells.J Diabetes. 2014 Sep;6(5):394-402. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12161. Epub 2014 May 22. J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24725840 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of DPP-4-protected GLP-1 (7-36) on coronary microvascular function in obese adults.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2019 Jan 29;22:139-144. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2019.01.004. eCollection 2019 Mar. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2019. PMID: 30740510 Free PMC article.
-
High Doses of Exogenous Glucagon Stimulate Insulin Secretion and Reduce Insulin Clearance in Healthy Humans.Diabetes. 2024 Mar 1;73(3):412-425. doi: 10.2337/db23-0201. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38015721 Free PMC article.
-
Is GLP-1 a hormone: Whether and When?J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):50-5. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12466. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the incretin effect in healthy subjects: concordance between clamp and OGTT methods.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Oct 1;325(4):E412-E420. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00104.2022. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37702736 Free PMC article.
-
The incretin co-agonist tirzepatide requires GIPR for hormone secretion from human islets.Nat Metab. 2023 Jun;5(6):945-954. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00811-0. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 37277609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Creutzfeldt W. The incretin concept today. Diabetologia. 1979;16:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ. Both GLP-1 and GIP are insulinotropic at basal and postprandial glucose levels and contribute nearly equally to the incretin effect of a meal in healthy subjects. Regul Pept. 2003;114:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Scrocchi LA, Brown TJ, MaClusky N, et al. Glucose intolerance but normal satiety in mice with a null mutation in the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene. Nat Med. 1996;2:1254–1258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

