GW5074 and PP2 kinase inhibitors implicate nontraditional c-Raf and Lyn function as drivers of retinoic acid-induced maturation
- PMID: 25817574
- PMCID: PMC4529126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.03.014
GW5074 and PP2 kinase inhibitors implicate nontraditional c-Raf and Lyn function as drivers of retinoic acid-induced maturation
Abstract
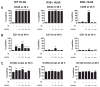
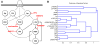
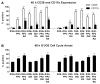
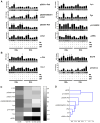
The multivariate nature of cancer necessitates multi-targeted therapy, and kinase inhibitors account for a vast majority of approved cancer therapeutics. While acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients are highly responsive to retinoic acid (RA) therapy, kinase inhibitors have been gaining momentum as co-treatments with RA for non-APL acute myeloid leukemia (AML) differentiation therapies, especially as a means to treat relapsed or refractory AML patients. In this study GW5074 (a c-Raf inhibitor) and PP2 (a Src-family kinase inhibitor) enhanced RA-induced maturation of t(15;17)-negative myeloblastic leukemia cells and rescued response in RA-resistant cells. PD98059 (a MEK inhibitor) and Akti-1/2 (an Akt inhibitor) were less effective, but did tend to promote maturation-uncoupled G1/G0 arrest, while wortmannin (a PI3K inhibitor) did not enhance differentiation surface marker expression or growth arrest. PD98059 and Akti-1/2 did not enhance differentiation markers and have potential, antagonistic off-targets effects on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), but neither could the AhR agonist 6-formylindolo(3,2-b)carbazole (FICZ) rescue differentiation events in the RA-resistant cells. GW5074 rescued early CD38 expression in RA-resistant cells exhibiting an early block in differentiation before CD38 expression, while for RA-resistant cells with differentiation blocked later, PP2 rescued the later differentiation marker CD11b; but surprisingly, the combination of the two was not synergistic. Kinases c-Raf, Src-family kinases Lyn and Fgr, and PI3K display highly correlated signaling changes during RA treatment, while activation of traditional downstream targets (Akt, MEK/ERK), and even the surface marker CD38, were poorly correlated with c-Raf or Lyn during differentiation. This suggests that an interrelated kinase module involving c-Raf, PI3K, Lyn and perhaps Fgr functions in a nontraditional way during RA-induced maturation or during rescue of RA induction therapy using inhibitor co-treatment in RA-resistant leukemia cells.
Keywords: Inhibitors; Leukemia; Lyn; Resistance; Retinoic acid; c-Raf.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Src-family kinase inhibitor PP2 rescues inducible differentiation events in emergent retinoic acid-resistant myeloblastic leukemia cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058621. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554907 Free PMC article.
-
Src inhibitors, PP2 and dasatinib, increase retinoic acid-induced association of Lyn and c-Raf (S259) and enhance MAPK-dependent differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells.Leukemia. 2012 Jun;26(6):1180-8. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.390. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Leukemia. 2012. PMID: 22182854 Free PMC article.
-
Roscovitine enhances All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced leukemia cell differentiation: Novel effects on signaling molecules for a putative Cdk2 inhibitor.Cell Signal. 2020 Jul;71:109555. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109555. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32032659
-
Kinase Inhibitors and Interferons as Other Myeloid Differentiation Inducers in Leukemia Therapy.Acta Haematol. 2022;145(2):113-121. doi: 10.1159/000519769. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Acta Haematol. 2022. PMID: 34673646 Review.
-
Mechanisms of all-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.J Biosci. 2000 Sep;25(3):275-84. doi: 10.1007/BF02703936. J Biosci. 2000. PMID: 11022230 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoic acid and 6-formylindolo(3,2-b)carbazole (FICZ) combination therapy reveals putative targets for enhancing response in non-APL AML.Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jul;60(7):1697-1708. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1543880. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019. PMID: 30570341 Free PMC article.
-
An Effective Model of the Retinoic Acid Induced HL-60 Differentiation Program.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 30;7(1):14327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14523-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29085021 Free PMC article.
-
Src family kinase inhibitor bosutinib enhances retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Dec;59(12):2941-2951. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1452213. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 29569971 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for subsets of wt-NPM1 primary AML blasts to respond to retinoic acid treatment.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 23;9(3):4134-4149. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23642. eCollection 2018 Jan 9. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29423110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf RC, Long J, Laidler P, Mijatovic S, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Stivala F, Mazzarino MC, Donia M, Fagone P, Malaponte G, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Milella M, Tafuri A, Bonati A, Bäsecke J, Cocco L, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Montalto G, Cervello M, McCubrey JA. Aging. 2011;3(3):192–222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martelli AM, Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Bortul R, Billi AM, Manzoli L, Ruggeri A, Conte R, Cocco L. Leukemia. 2003;17(9):1794–1805. - PubMed
-
- Tang X, Gudas LJ. Annu Rev Pathol: Mech. 2011;6:345–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

