Induction of potent adaptive immunity by the novel polyion complex nanoparticles
- PMID: 25809631
- PMCID: PMC4412939
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00080-15
Induction of potent adaptive immunity by the novel polyion complex nanoparticles
Abstract
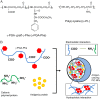
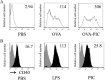
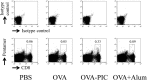
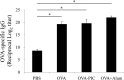
The development of effective and simple methods of vaccine preparation is desired for the prophylaxis and treatment of a variety of infectious diseases and cancers. We have created novel polyion complex (PIC) nanoparticles (NPs) composed of amphiphilic anionic biodegradable poly(γ-glutamic acid) (γ-PGA) and cationic polymers as a vaccine adjuvant. PIC NPs can be prepared by mixing γ-PGA-graft-l-phenylalanine ethylester (γ-PGA-Phe) polymer with cationic polymer in phosphate-buffered saline. We examined the efficacy of PIC NPs for antigen delivery and immunostimulatory activity in vitro and in vivo. PIC NPs enhanced the uptake of ovalbumin (OVA) by dendritic cells (DCs) and subsequently induced DC maturation. The immunization of mice with OVA-carrying PIC NPs induced potent and antigen-specific cellular and humoral immunity. Since PIC NPs can be created with water-soluble anionic γ-PGA-Phe and a cationic polymer by simple mixing in the absence of any organic solvents, PIC NPs may have potential as a novel candidate for an effective antigen carrier and vaccine adjuvant.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

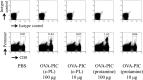
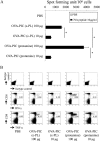
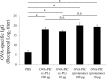
Similar articles
-
Manipulating the antigen-specific immune response by the hydrophobicity of amphiphilic poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanoparticles.Biomaterials. 2013 Dec;34(37):9709-16. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.064. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 24016848
-
Comparative activity of biodegradable nanoparticles with aluminum adjuvants: antigen uptake by dendritic cells and induction of immune response in mice.Immunol Lett. 2011 Oct 30;140(1-2):36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21693134
-
Effect of Hydrophobic Side Chains in the Induction of Immune Responses by Nanoparticle Adjuvants Consisting of Amphiphilic Poly(γ-glutamic acid).Bioconjug Chem. 2015 May 20;26(5):890-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00106. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Bioconjug Chem. 2015. PMID: 25865284
-
[Efficacy and safety of poly (gamma-glutamic acid) based nanoparticles (gamma-PGA NPs) as vaccine carrier].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Nov;128(11):1559-65. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.1559. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18981690 Review. Japanese.
-
Poly-γ-glutamic acid nanoparticles as adjuvant and antigen carrier system for cancer vaccination.J Control Release. 2023 Oct;362:278-296. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.049. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37640110 Review.
Cited by
-
Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Vaccine Adjuvants and Delivery Vehicles.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021;433:29-76. doi: 10.1007/82_2020_226. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33165869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradable polymers for modern vaccine development.J Ind Eng Chem. 2019 Sep 25;77:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2019.04.044. Epub 2019 Apr 28. J Ind Eng Chem. 2019. PMID: 32288512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The era of bioengineering: how will this affect the next generation of cancer immunotherapy?J Transl Med. 2017 Jun 19;15(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1244-2. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28629381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

