Cell cycle gene expression networks discovered using systems biology: Significance in carcinogenesis
- PMID: 25808367
- PMCID: PMC4481160
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24990
Cell cycle gene expression networks discovered using systems biology: Significance in carcinogenesis
Abstract
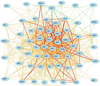
The early stages of carcinogenesis are linked to defects in the cell cycle. A series of cell cycle checkpoints are involved in this process. The G1/S checkpoint that serves to integrate the control of cell proliferation and differentiation is linked to carcinogenesis and the mitotic spindle checkpoint is associated with the development of chromosomal instability. This paper presents the outcome of systems biology studies designed to evaluate if networks of covariate cell cycle gene transcripts exist in proliferative mammalian tissues including mice, rats, and humans. The GeneNetwork website that contains numerous gene expression datasets from different species, sexes, and tissues represents the foundational resource for these studies (www.genenetwork.org). In addition, WebGestalt, a gene ontology tool, facilitated the identification of expression networks of genes that co-vary with key cell cycle targets, especially Cdc20 and Plk1 (www.bioinfo.vanderbilt.edu/webgestalt). Cell cycle expression networks of such covariate mRNAs exist in multiple proliferative tissues including liver, lung, pituitary, adipose, and lymphoid tissues among others but not in brain or retina that have low proliferative potential. Sixty-three covariate cell cycle gene transcripts (mRNAs) compose the average cell cycle network with P = e(-13) to e(-36) . Cell cycle expression networks show species, sex and tissue variability, and they are enriched in mRNA transcripts associated with mitosis, many of which are associated with chromosomal instability.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No Conflict of Interest
Figures
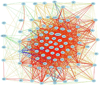
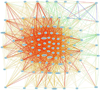
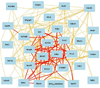
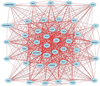

Similar articles
-
Toward a systems-level view of mitotic checkpoints.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;117(2-3):217-224. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25722206 Review.
-
[Prognostic Value of PCMT1 Expression in Gastric Cancer and Its Regulatory Effect on Spindle Assembly Checkpoints].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Nov 20;54(6):1167-1175. doi: 10.12182/20231160211. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38162070 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Mammalian neurogenesis requires Treacle-Plk1 for precise control of spindle orientation, mitotic progression, and maintenance of neural progenitor cells.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(3):e1002566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002566. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22479190 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with chromosomal instability.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 15;12(2):405-10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0903. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16428479
-
Working on Genomic Stability: From the S-Phase to Mitosis.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;11(2):225. doi: 10.3390/genes11020225. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093406 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro anticancer study of novel curcumin derivatives via targeting PI3K/Akt/p53 signaling pathway.Mol Divers. 2024 Jul 1. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10833-9. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38951417
-
Preexisting Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Blunts the Development of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis.JBMR Plus. 2022 Apr 19;6(5):e10625. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10625. eCollection 2022 May. JBMR Plus. 2022. PMID: 35509635 Free PMC article.
-
Pin1 inhibition potently suppresses gastric cancer growth and blocks PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin oncogenic pathways.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Aug;58(8):1450-1464. doi: 10.1002/mc.23027. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31026381 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptome analyses reveal novel targets modulating cardiac neovascularization by resident endothelial cells following myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 2019 Aug 7;40(30):2507-2520. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz305. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31162546 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA-Seq reveals changes in immune landscape in post-traumatic osteoarthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 29;13:938075. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.938075. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar R, Grandy R, Meza D, Sepulveda H, Pihan P, van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Stein GS, Stein JL, Montecino M. A functional N-terminal domain in C/EBPbeta-LAP* is required for interacting with SWI/SNF and to repress Ric-8B gene transcription in osteoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014;229:1521–1528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aziz F, van Wijnen aJ, Stein JL, Stein GS. HiNF-D (CDP-cut/CDC2/cyclin A/pRB-complex) influences the timing of IRF-2-dependent cell cycle activation of human histone H4 gene transcription at the G1/S phase transition. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998;177:453–464. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199812)177:3<453::AID-JCP8>3.0.CO;2-F. - PubMed
-
- Blagosklonny MV, Pardee AB. The restriction point of the cell cycle. cc. 2002;1:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

