Physiological implications of biased signaling at histamine H2 receptors
- PMID: 25805997
- PMCID: PMC4354273
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00045
Physiological implications of biased signaling at histamine H2 receptors
Abstract
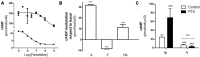
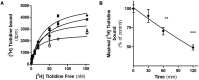
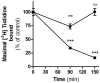
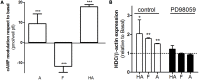
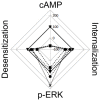
Histamine mediates numerous functions acting through its four receptor subtypes all belonging to the large family of seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors. In particular, histamine H2 receptor (H2R) is mainly involved in gastric acid production, becoming a classic pharmacological target to treat Zollinger-Ellison disease and gastric and duodenal ulcers. H2 ligands rank among the most widely prescribed and over the counter-sold drugs in the world. Recent evidence indicate that some H2R ligands display biased agonism, selecting and triggering some, but not all, of the signaling pathways associated to the H2R. The aim of the present work is to study whether famotidine, clinically widespread used ligand acting at H2R, exerts biased signaling. Our findings indicate that while famotidine acts as inverse agonist diminishing cAMP basal levels, it mimics the effects of histamine and the agonist amthamine concerning receptor desensitization and internalization. Moreover, the treatment of HEK293T transfected cells with any of the three ligands lead to a concentration dependent pERK increment. Similarly in AGS gastric epithelial cells, famotidine treatment led to both, the reduction in cAMP levels as well as the increment in ERK phosphorylation, suggesting that this behavior could have pharmacological relevant implications. Based on that, histidine decarboxylase expression was studied by quantitative PCR in AGS cells and its levels were increased by famotidine as well as by histamine and amthamine. In all cases, the positive regulation was impeded by the MEK inhibitor PD98059, indicating that biased signaling toward ERK1/2 pathway is the responsible of such enzyme regulation. These results support that ligand bias is not only a pharmacological curiosity but has physiological and pharmacological implications on cell metabolism.
Keywords: 7TMR; ERK; GPCR internalization; H2R ligands; HDC; biased agonism; pluridimensional efficacy.
Figures
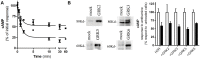

Similar articles
-
Signal transduction mechanism of biased ligands at histamine H2 receptors.Biochem J. 2014 Apr 1;459(1):117-26. doi: 10.1042/BJ20131226. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 24417223
-
PI3K pathway is involved in ERK signaling cascade activation by histamine H2R agonist in HEK293T cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1860(9):1998-2007. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27316323
-
Histamine H2 receptor trafficking: role of arrestin, dynamin, and clathrin in histamine H2 receptor internalization.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;74(4):1109-18. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.045336. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18617631
-
Famotidine. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and a preliminary review of its therapeutic use in peptic ulcer disease and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.Drugs. 1986 Sep;32(3):197-221. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198632030-00001. Drugs. 1986. PMID: 2875864 Review.
-
Histamine H2 receptor radioligands: triumphs and challenges.Future Med Chem. 2021 Jun;13(12):1073-1081. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2021-0058. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Future Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33906421 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Oral Famotidine in Patients Hospitalized With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.Cureus. 2022 Feb 20;14(2):e22404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22404. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35345695 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: Famotidine, Histamine, Mast Cells, and Mechanisms.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 31:rs.3.rs-30934. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-30934/v2. Res Sq. 2020. Update in: Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 23;12:633680. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.633680 PMID: 32702719 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Famotidine promotes inflammation by triggering cell pyroptosis in gastric cancer cells.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Oct 22;22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00533-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34686215 Free PMC article.
-
Design and development of novel, short, stable dynorphin-based opioid agonists for safer analgesic therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1150313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1150313. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937883 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Cardiovascular H2-Histamine Receptors Under Normal and Pathophysiological Conditions.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 20;12:732842. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.732842. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34987383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakker R. A., Timmerman H., Leurs R. (2002). Histamine receptors: specific ligands, receptor biochemistry, and signal transduction. Clin. Allergy Immunol. 17 27–64. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

