The effects of exendin-4 treatment on graft failure: an animal study using a novel re-vascularized minimal human islet transplant model
- PMID: 25793295
- PMCID: PMC4368803
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121204
The effects of exendin-4 treatment on graft failure: an animal study using a novel re-vascularized minimal human islet transplant model
Abstract
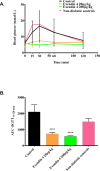
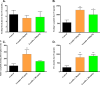
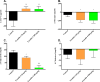
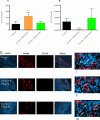
Islet transplantation has become a viable clinical treatment, but is still compromised by long-term graft failure. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, has in clinical studies been shown to improve insulin secretion in islet transplanted patients. However, little is known about the effect of exendin-4 on other metabolic parameters. We therefore aimed to determine what influence exendin-4 would have on revascularized minimal human islet grafts in a state of graft failure in terms of glucose metabolism, body weight, lipid levels and graft survival. Introducing the bilateral, subcapsular islet transplantation model, we first transplanted diabetic mice with a murine graft under the left kidney capsule sufficient to restore normoglycemia. After a convalescent period, we performed a second transplantation under the right kidney capsule with a minimal human islet graft and allowed for a second recovery. We then performed a left-sided nephrectomy, and immediately started treatment with exendin-4 with a low (20μg/kg/day) or high (200μg/kg/day) dose, or saline subcutaneously twice daily for 15 days. Blood was sampled, blood glucose and body weight monitored. The transplanted human islet grafts were collected at study end point and analyzed. We found that exendin-4 exerts its effect on failing human islet grafts in a bell-shaped dose-response curve. Both doses of exendin-4 equally and significantly reduced blood glucose. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), C-peptide and pro-insulin were conversely increased. In the course of the treatment, body weight and cholesterol levels were not affected. However, immunohistochemistry revealed an increase in beta cell nuclei count and reduced TUNEL staining only in the group treated with a low dose of exendin-4 compared to the high dose and control. Collectively, these results suggest that exendin-4 has a potential rescue effect on failing, revascularized human islets in terms of lowering blood glucose, maintaining beta cell numbers, and improving metabolic parameters during hyperglycemic stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo treatment with glucagon-like peptide 1 promotes the graft function of fetal islet-like cell clusters in transplanted mice.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):951-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.08.005. Epub 2005 Sep 7. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16172015
-
Exendin-4 treatment expands graft beta-cell mass in diabetic mice transplanted with a marginal number of fresh islets.Cell Transplant. 2008;17(6):641-7. doi: 10.3727/096368908786092766. Cell Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18819252
-
Exendin-4 treatment improves metabolic control after rat islet transplantation to athymic mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Diabetologia. 2006 Jun;49(6):1247-53. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0251-2. Epub 2006 Apr 12. Diabetologia. 2006. PMID: 16609877
-
Pharmacology of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4): a potential therapeutic for improved glycemic control of type 2 diabetes.Regul Pept. 2004 Feb 15;117(2):77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2003.10.028. Regul Pept. 2004. PMID: 14700743 Review.
-
64Cu-Labeled 1,4,7-tris(acetic acid)-10-vinylsulfone-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane conjugated to Cys40-Exendin-4.2011 Aug 24 [updated 2012 Mar 15]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Aug 24 [updated 2012 Mar 15]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22439162 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Preserve Pancreatic Islet Function in a Transplantable 3D Bioprinted Scaffold.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Dec;12(32):e2300640. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202300640. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37781993 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the prostaglandin D2-GPR44/DP2 axis improves human islet survival and function.Diabetologia. 2020 Jul;63(7):1355-1367. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05138-z. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32350565 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SGLT2 Preserves Function and Promotes Proliferation of Human Islets Cells In Vivo in Diabetic Mice.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 18;10(2):203. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020203. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203411 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell secretory molecules improve the functional survival of human islets.Diabet Med. 2023 Dec;40(12):e15227. doi: 10.1111/dme.15227. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Diabet Med. 2023. PMID: 37728506 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1-Induced AMPK Activation Inhibits PARP-1 and Promotes LXR-Mediated ABCA1 Expression to Protect Pancreatic β-Cells Against Cholesterol-Induced Toxicity Through Cholesterol Efflux.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 7;9:646113. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646113. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34307343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Adra DP, Gill RS, Imes S, O'Gorman D, Kin T, Axford SJ, et al. (2014) Single-Donor Islet Transplantation and Long-term Insulin Independence in Select Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Transplantation. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

