Link between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: from epidemiology to mechanism and treatment
- PMID: 25792818
- PMCID: PMC4360697
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S74042
Link between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: from epidemiology to mechanism and treatment
Abstract
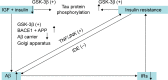
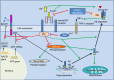
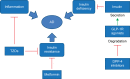
The aim of this paper is to provide a comprehensive review of the epidemiological evidence linking type 2 diabetes mellitus and its related conditions, including obesity, hyperinsulinemia, and metabolic syndrome, to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Several mechanisms could help to explain this proposed link; however, our focus is on insulin resistance and deficiency. Studies have shown that insulin resistance and deficiency can interact with amyloid-β protein and tau protein phosphorylation, each leading to the onset and development of AD. Based on those epidemiological data and basic research, it was recently proposed that AD can be considered as "type 3 diabetes". Special attention has been paid to determining whether antidiabetic agents might be effective in treating AD. There has been much research both experimental and clinical on this topic. We mainly discuss the clinical trials on insulin, metformin, thiazolidinediones, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of AD. Although the results of these trials seem to be contradictory, this approach is also full of promise. It is worth mentioning that the therapeutic effects of these drugs are influenced by the apolipoprotein E (APOE)-ε4 genotype. Patients without the APOE-ε4 allele showed better treatment effects than those with this allele.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; insulin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Comment in
-
Importance of hypoglycemia on the risk of Alzheimer's disease in elderly subjects with diabetes mellitus.Clin Interv Aging. 2015 Nov 3;10:1789-91. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S93925. eCollection 2015. Clin Interv Aging. 2015. PMID: 26622173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Diabetes drugs in the fight against Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Sep;54:100936. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100936. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31330313 Review.
-
Antidiabetic drugs and their potential role in treating mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Discov Med. 2013 Dec;16(90):277-86. Discov Med. 2013. PMID: 24333407 Review.
-
Peripheral insulin-sensitizer drug metformin ameliorates neuronal insulin resistance and Alzheimer's-like changes.Neuropharmacology. 2011 May;60(6):910-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.033. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21277873
-
Crosstalk between Alzheimer's disease and diabetes: a focus on anti-diabetic drugs.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Aug;38(6):1769-1800. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01225-3. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37335453 Review.
-
Therapy Insight: type 2 diabetes mellitus and the risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006 Mar;2(3):159-66. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0124. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16932542 Review.
Cited by
-
Type 2 diabetes is associated with increased risk of dementia, but not mild cognitive impairment: a cross-sectional study among the elderly in Chinese communities.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 16;14:1004954. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1004954. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36185492 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases: towards the development of effective therapy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jul;476(7):2739-2752. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04120-6. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33687588 Review.
-
Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease-related diseases, cognition and dementia: A two-sample mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 29;19(2):e0297883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297883. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38422093 Free PMC article.
-
Rosiglitazone has a neutral effect on the risk of dementia in type 2 diabetes patients.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 May 14;11(9):2724-2734. doi: 10.18632/aging.101944. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31085804 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induces Tau Hyperphosphorylation in Rat Brain.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024 Apr 8;8(1):615-626. doi: 10.3233/ADR-240040. eCollection 2024. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 38746631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Marioni RE, Price JF. Cognitive function, dementia and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7(2):108–114. - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(1):64–74. - PubMed
-
- Cukierman T, Gerstein H, Williamson J. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes – systematic overview of prospective observational studies. Diabetologia. 2005;48(12):2460–2469. - PubMed
-
- Strachan MW, Deary IJ, Ewing FM, Frier BM. Is type II diabetes associated with an increased risk of cognitive dysfunction? A critical review of published studies. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(3):438–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

