TBCRC 019: A Phase II Trial of Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel with or without the Anti-Death Receptor 5 Monoclonal Antibody Tigatuzumab in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 25779953
- PMCID: PMC6186432
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2780
TBCRC 019: A Phase II Trial of Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel with or without the Anti-Death Receptor 5 Monoclonal Antibody Tigatuzumab in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
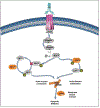
Purpose: Tigatuzumab (TIG), an agonistic anti-DR5 antibody, triggers apoptosis in DR5(+) human tumor cells without crosslinking. TIG has strong in vitro/in vivo activity against basal-like breast cancer cells enhanced by chemotherapy agents. This study evaluates activity of TIG and chemotherapy in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Experimental design: Randomized 2:1 phase II trial of albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-PAC) ± TIG in patients with TNBC stratified by prior chemotherapy. Patients received nab-PAC weekly × 3 ± TIG every other week, every 28 days. Primary objective was within-arm objective response rate (ORR). Secondary objectives were safety, progression-free survival (PFS), clinical benefit, and TIG immunogenicity. Metastatic research biopsies were required.
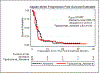
Results: Among 64 patients (60 treated; TIG/nab-PAC n = 39 and nab-PAC n = 21), there were 3 complete remissions (CR), 8 partial remissions (PR; 1 almost CR), 11 stable diseases (SD), and 17 progressive diseases (PD) in the TIG/nab-PAC arm (ORR, 28%), and no CRs, 8 PRs, 4 SDs, and 9 PDs in the nab-PAC arm (ORR, 38%). There was a numerical increase in CRs and several patients had prolonged PFS (1,025+, 781, 672, 460, 334) in the TIG/nab-PAC arm. Grade 3 toxicities were 28% and 29%, respectively, with no grade 4-5. Exploratory analysis suggests an association of ROCK1 gene pathway activation with efficacy in the TIG/nab-PAC arm.
Conclusions: ORR and PFS were similar in both. Preclinical activity of TIG in basal-like breast cancer and prolonged PFS in few patients in the combination arm support further investigation of anti-DR5 agents. ROCK pathway activation merits further evaluation.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nab-paclitaxel/bevacizumab/carboplatin chemotherapy in first-line triple negative metastatic breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2013 Dec;13(6):416-20. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24099649 Clinical Trial.
-
Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 29;379(22):2108-2121. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809615. Epub 2018 Oct 20. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30345906 Clinical Trial.
-
Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients within a Randomized, Phase II Trial: TBCRC 019.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 15;21(12):2771-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2781. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25779948 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nab-paclitaxel for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer: Rationale, clinical data and future perspectives.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Nov;50:129-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 27665540 Review.
-
Atezolizumab (in Combination with Nab-Paclitaxel): A Review in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Drugs. 2020 Apr;80(6):601-607. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01295-y. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32248356 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Advancements of Plant-Derived Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy through Deregulating Cancer Cell Functions and Reprogramming Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13571. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413571. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyproterone acetate enhances TRAIL-induced androgen-independent prostate cancer cell apoptosis via up-regulation of death receptor 5.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 7;17(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3153-4. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28270124 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Anlotinib combined with PD-1 inhibitor and sequential GA regimen or FOLFIRINOX Chemotherapy in treatment of KRAS G12V mutated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with liver metastasis: A case and literature review.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1016647. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1016647. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent insights in nanotechnology-based drugs and formulations designed for effective anti-cancer therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2016 May 26;14(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12951-016-0193-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016. PMID: 27229857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting PDK4 inhibits breast cancer metabolism.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 1;8(9):1725-1738. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30323966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406: 747–752. - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98: 10869–10874. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montagna E, Maisonneuve P, Rotmensz N, Cancello G, Iorfida M, Balduzzi A, Galimberti V, Veronesi P, Luini A, Pruneri G, Bottiglieri L, Mastropasqua MG, Goldhirsch A, Viale G, Colleoni M: Heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer: histologic subtyping to inform the outcome. Clin Breast Cancer 2013, 13: 31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

