Characterization of CD8+ T cell differentiation following SIVΔnef vaccination by transcription factor expression profiling
- PMID: 25768938
- PMCID: PMC4358830
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004740
Characterization of CD8+ T cell differentiation following SIVΔnef vaccination by transcription factor expression profiling
Erratum in
-
Correction: Characterization of CD8+ T Cell Differentiation following SIVΔnef Vaccination by Transcription Factor Expression Profiling.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jun 11;11(6):e1004968. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004968. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26068217 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
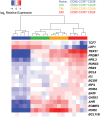
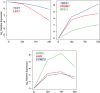
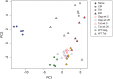
The onset of protective immunity against pathogenic SIV challenge in SIVΔnef-vaccinated macaques is delayed for 15-20 weeks, a process that is related to qualitative changes in CD8+ T cell responses induced by SIVΔnef. As a novel approach to characterize cell differentiation following vaccination, we used multi-target qPCR to measure transcription factor expression in naïve and memory subsets of CD8++ T cells, and in SIV-specific CD8+ T cells obtained from SIVΔnef-vaccinated or wild type SIVmac239-infected macaques. Unsupervised clustering of expression profiles organized naïve and memory CD8+ T cells into groups concordant with cell surface phenotype. Transcription factor expression patterns in SIV-specific CD8+ T cells in SIVΔnef-vaccinated animals were distinct from those observed in purified CD8+ T cell subsets obtained from naïve animals, and were intermediate to expression profiles of purified central memory and effector memory T cells. Expression of transcription factors elicited by SIVΔnef vaccination also varied over time: cells obtained at later time points, temporally associated with greater protection, appeared more central-memory like than cells obtained at earlier time points, which appeared more effector memory-like. Expression of transcription factors associated with effector differentiation, such as ID2 and RUNX3, were decreased over time, while expression of transcription factors associated with quiescence or memory differentiation, such as TCF7, BCOR and EOMES, increased. CD8+ T cells specific for a more conserved epitope expressed higher levels of TBX21 and BATF, and appeared more effector-like than cells specific for an escaped epitope, consistent with continued activation by replicating vaccine virus. These data suggest transcription factor expression profiling is a novel method that can provide additional data complementary to the analysis of memory cell differentiation based on classical phenotypic markers. Additionally, these data support the hypothesis that ongoing stimulation by SIVΔnef promotes a distinct protective balance of CD8+ T cell differentiation and activation states.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
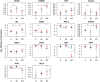
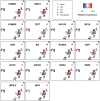
Similar articles
-
Distinct transcriptome profiles of Gag-specific CD8+ T cells temporally correlated with the protection elicited by SIVΔnef live attenuated vaccine.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 23;12(3):e0173929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173929. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28333940 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Low-Level Replication of SIVΔnef Drives Maturation of Antibody and CD8 T Cell Responses to Induce Protective Immunity against Vaginal SIV Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Dec 13;12(12):e1006104. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006104. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27959961 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic vaccination with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-DNA + IL-12 or IL-15 induces distinct CD8 memory subsets in SIV-infected macaques.J Immunol. 2008 Jun 15;180(12):7969-79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.12.7969. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18523260 Clinical Trial.
-
Running to Stand Still: Naive CD8+ T Cells Actively Maintain a Program of Quiescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 21;21(24):9773. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249773. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33371448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generating diversity: transcriptional regulation of effector and memory CD8 T-cell differentiation.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):219-33. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00901.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536566 Review.
Cited by
-
Microraft arrays for serial-killer CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells and single cell isolation.Cytometry A. 2023 Mar;103(3):208-220. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.24678. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Cytometry A. 2023. PMID: 35899783 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional rewiring in CD8+ T cells: implications for CAR-T cell therapy against solid tumours.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1412731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1412731. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39399500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Concepts for HIV Vaccine Vector Design.mSphere. 2017 Dec 6;2(6):e00415-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00415-17. eCollection 2017 Nov-Dec. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 29242831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct transcriptome profiles of Gag-specific CD8+ T cells temporally correlated with the protection elicited by SIVΔnef live attenuated vaccine.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 23;12(3):e0173929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173929. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28333940 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating β cell-specific CD8+ T cells restricted by high-risk HLA class I molecules show antigen experience in children with and at risk of type 1 diabetes.Clin Exp Immunol. 2020 Mar;199(3):263-277. doi: 10.1111/cei.13391. Epub 2019 Nov 10. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31660582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daniel MD, Kirchhoff F, Czajak SC, Sehgal PK, Desrosiers RC (1992) Protective effects of a live attenuated SIV vaccine with a deletion in the nef gene. Science 258: 1938–1941. - PubMed
-
- Almond N, Kent K, Cranage M, Rud E, Clarke B, et al. (1995) Protection by attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus in macaques against challenge with virus-infected cells. Lancet 345: 1342–1344. - PubMed
-
- Baba TW, Liska V, Khimani AH, Ray NB, Dailey PJ, et al. (1999) Live attenuated, multiply deleted simian immunodeficiency virus causes AIDS in infant and adult macaques. Nat Med 5: 194–203. - PubMed
-
- Baba TW, Jeong YS, Pennick D, Bronson R, Greene MF, et al. (1995) Pathogenicity of live, attenuated SIV after mucosal infection of neonatal macaques. Science 267: 1820–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

