The role of miR-29b in cancer: regulation, function, and signaling
- PMID: 25767398
- PMCID: PMC4354468
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S75899
The role of miR-29b in cancer: regulation, function, and signaling
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small non-coding RNAs with the capacity to regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally. The miRNA-29 family consists of miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c, among which miR-29b is the most highly expressed and is found at two genomic loci. Recently, numerous studies have demonstrated that aberrant expression of miR-29b is common in the majority of human cancers. miR-29b is known to critically affect cancer progression by functioning as a tumor suppressor. However, it may also act as an oncogene under certain conditions. In this review, we illustrate the role of miR-29b in cancer regulation, function, and signaling. This is the first review highlighting the role of miR-29b in cancer. Our review aims to summarize the effects of miR-29b on cancer activity and its interactions with target genes and signaling pathways, as well as to provide therapeutic implications for overcoming cancer chemoresistance.
Keywords: biological function; cancer; chemoresistance; miR-29b; oncogene; tumor promoter.
Figures
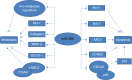
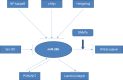
Similar articles
-
microRNA-29b: an emerging player in human cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(21):9059-64. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.21.9059. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25422179 Review.
-
MiRNA-29: a microRNA family with tumor-suppressing and immune-modulating properties.Curr Mol Med. 2013 May;13(4):572-85. doi: 10.2174/1566524011313040009. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 22934851 Review.
-
Mir-29b in Breast Cancer: A Promising Target for Therapeutic Approaches.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2139. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092139. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of EZH2 triggers the tumor suppressive miR-29b network in multiple myeloma.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 20;8(63):106527-106537. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22507. eCollection 2017 Dec 5. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29290968 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miRNA-29 family in cancer.Eur J Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;92(3):123-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2012.11.004. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23357522 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ticking of the Epigenetic Clock: Antipsychotic Drugs in Old Age.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Aug 31;7:122. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00122. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27630617 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of MicroRNAs With In Vivo Efficacy in Multiple Myeloma-related Xenograft Models.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020 Jul-Aug;17(4):321-334. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20192. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32576578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation and Dietary Control of Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Front Nutr. 2020 Sep 8;7:159. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00159. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33015128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 Apr 15;8(4):330-40. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i4.330. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27096028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin-upregulated miR-29b promotes mTORC1-hyperactive cell growth in TSC2-deficient cells by downregulating tumor suppressor retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ).Oncogene. 2019 Dec;38(49):7367-7383. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0957-5. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 31420607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(3):118–126. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(2):102–114. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

