K2P channel gating mechanisms revealed by structures of TREK-2 and a complex with Prozac
- PMID: 25766236
- PMCID: PMC6034649
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1261512
K2P channel gating mechanisms revealed by structures of TREK-2 and a complex with Prozac
Abstract
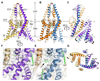
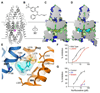
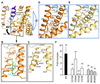
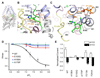
TREK-2 (KCNK10/K2P10), a two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channel, is gated by multiple stimuli such as stretch, fatty acids, and pH and by several drugs. However, the mechanisms that control channel gating are unclear. Here we present crystal structures of the human TREK-2 channel (up to 3.4 angstrom resolution) in two conformations and in complex with norfluoxetine, the active metabolite of fluoxetine (Prozac) and a state-dependent blocker of TREK channels. Norfluoxetine binds within intramembrane fenestrations found in only one of these two conformations. Channel activation by arachidonic acid and mechanical stretch involves conversion between these states through movement of the pore-lining helices. These results provide an explanation for TREK channel mechanosensitivity, regulation by diverse stimuli, and possible off-target effects of the serotonin reuptake inhibitor Prozac.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bilayer-Mediated Structural Transitions Control Mechanosensitivity of the TREK-2 K2P Channel.Structure. 2017 May 2;25(5):708-718.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Structure. 2017. PMID: 28392258 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Structural Basis of the Intracellular pH Sensing Mechanism of TASK-2 K2P Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 14;21(2):532. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020532. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31947679 Free PMC article.
-
K2P2.1 (TREK-1)-activator complexes reveal a cryptic selectivity filter binding site.Nature. 2017 Jul 20;547(7663):364-368. doi: 10.1038/nature22988. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28693035 Free PMC article.
-
Gating, Regulation, and Structure in K2P K+ Channels: In Varietate Concordia?Mol Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;90(3):309-17. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.103895. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27268784 Review.
-
Molecular Pharmacology of K2P Potassium Channels.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Mar 6;55(S3):87-107. doi: 10.33594/000000339. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33667333 Review.
Cited by
-
Heavy Atom Detergent/Lipid Combined X-ray Crystallography for Elucidating the Structure-Function Relationships of Membrane Proteins.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;11(11):823. doi: 10.3390/membranes11110823. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-life serotonin dysregulation affects the migration and positioning of cortical interneuron subtypes.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Sep 22;5(9):e644. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.147. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26393490 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Potassium Channels Inhibits Bunyavirus Infection.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3411-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.692673. Epub 2015 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26677217 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric coupling between proximal C-terminus and selectivity filter is facilitated by the movement of transmembrane segment 4 in TREK-2 channel.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 16;6:21248. doi: 10.1038/srep21248. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26879043 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-canonical Voltage-Sensing Mechanism Controls Gating in K2P K(+) Channels.Cell. 2016 Feb 25;164(5):937-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.002. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26919430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Enyedi P, Czirjak G. Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:559–605. - PubMed
-
- Cohen A, Ben-Abu Y, Zilberberg N. Gating the pore of potassium leak channels. Eur Biophys J. 2009;39:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Dedman A, et al. The mechano-gated K(2P) channel TREK-1. Eur Biophys J. 2009;38:293–303. - PubMed
-
- Patel AJ, Honore E. 2P domain K+ channels: novel pharmacological targets for volatile general anesthetics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;536:9–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

