Histone deacetylase inhibition as an alternative strategy against invasive aspergillosis
- PMID: 25762988
- PMCID: PMC4329796
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00096
Histone deacetylase inhibition as an alternative strategy against invasive aspergillosis
Abstract
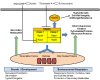
Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is a life-threatening infection due to Aspergillus fumigatus and other Aspergillus spp. Drugs targeting the fungal cell membrane (triazoles, amphotericin B) or cell wall (echinocandins) are currently the sole therapeutic options against IA. Their limited efficacy and the emergence of resistance warrant the identification of new antifungal targets. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are enzymes responsible of the deacetylation of lysine residues of core histones, thus controlling chromatin remodeling and transcriptional activation. HDACs also control the acetylation and activation status of multiple non-histone proteins, including the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90), an essential molecular chaperone for fungal virulence and antifungal resistance. This review provides an overview of the different HDACs in Aspergillus spp. as well as their respective contribution to total HDAC activity, fungal growth, stress responses, and virulence. The potential of HDAC inhibitors, currently under development for cancer therapy, as novel alternative antifungal agents against IA is discussed.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; antifungal resistance; antifungal therapy; heat shock protein 90; lysine deacetylases; trichostatin A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90): A novel antifungal target against Aspergillus fumigatus.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42(2):310-21. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.947239. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 25243616 Review.
-
A Class 1 Histone Deacetylase with Potential as an Antifungal Target.mBio. 2016 Nov 1;7(6):e00831-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00831-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27803184 Free PMC article.
-
Echinocandins for the Treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis: from Laboratory to Bedside.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jul 25;63(8):e00399-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00399-19. Print 2019 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31138565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifungal activity of compounds targeting the Hsp90-calcineurin pathway against various mould species.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015 May;70(5):1408-11. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku549. Epub 2015 Jan 3. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25558076
-
The contribution of Aspergillus fumigatus stress responses to virulence and antifungal resistance.J Microbiol. 2016 Mar;54(3):243-53. doi: 10.1007/s12275-016-5510-4. Epub 2016 Feb 27. J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26920884 Review.
Cited by
-
Aspergillus fumigatus, One Uninucleate Species with Disparate Offspring.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jan 6;7(1):30. doi: 10.3390/jof7010030. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33419224 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3, histone deacetylases, and Hedgehog signaling: Possible convergent targets in schistosomiasis-induced liver fibrosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Feb 23;11(2):e0005137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005137. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28231240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Approaches for Combating Aspergillus Associated Infection.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(16):1465-1488. doi: 10.2174/1389450123666220623164548. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 35748549 Review.
-
Unfolding antifungals: as a new foe to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-a mini-review.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Mar;48(3):2945-2956. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06318-9. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33796989 Review.
-
A Class 1 Histone Deacetylase as Major Regulator of Secondary Metabolite Production in Aspergillus nidulans.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 19;9:2212. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02212. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30283426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augenbraun M., Livingston J., Parker R., Lederman S., Chavoustie S., Morgan F., et al. (2013). “Fluconazole and MGCD290 in vulvo vaginal candidiasis (VVC): results from a randomized phase II study (1330),” in IDWeek 2013, October 2–6, 2013, San Francisco, CA.
-
- Bali P., Pranpat M., Bradner J., Balasis M., Fiskus W., Guo F., et al. (2005). Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 26729–26734. 10.1074/jbc.C500186200 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

