Lipidomics revealed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-induced hepatic lipid disorders corrected with treatment of baicalin in a murine model
- PMID: 25762447
- PMCID: PMC4406959
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-014-9714-4
Lipidomics revealed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-induced hepatic lipid disorders corrected with treatment of baicalin in a murine model
Abstract
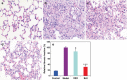
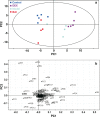
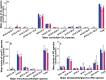
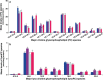
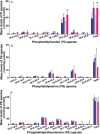
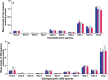
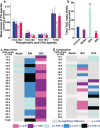
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fatal lung disease. The current standard treatment with glucocorticoids (GCs) leads to many adverse effects, and its effectiveness is questionable. Thus, it is critical and urgent to find new drug(s) for treatment of IPF. Baicalin (BAI) is an attractive candidate for this purpose. Herein, utilizing shotgun lipidomics, we revealed that IPF could lead to a lipid disorder of the liver in an animal model induced by bleomycin and confirmed through histopathological studies of the lung. Lipidomics further demonstrated that this disorder could virtually be corrected after treatment with BAI, but not with dexamethasone (DEX) (a commonly used GC for treatment of IPF). In contrast, the treatment with DEX did not improve IPF but led to tremendous alterations in hepatic lipidomes and accumulation of fat in the liver, which was very different from the lipid disorder induced by IPF. The underpinning mechanisms of the IPF-resultant lipid disorder and DEX-induced lipotoxicity as revealed by shotgun lipidomics were extensively discussed. Taken together, the current study showed that IPF could lead to hepatic lipid disorder, which can be treated with BAI, and demonstrated that lipidomics could be a powerful tool for drug screening.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of tissue lipidomics and computed tomography pulmonary fat attenuation volume (CTPFAV ) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respirology. 2023 Nov;28(11):1043-1052. doi: 10.1111/resp.14582. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Respirology. 2023. PMID: 37642207
-
Identification of the lipid biomarkers from plasma in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by Lipidomics.BMC Pulm Med. 2017 Dec 6;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0513-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2017. PMID: 29212488 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to therapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Aug;101(8):905-915. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02336-1. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37289208 Review.
-
Bleomycin Induces Drug Efflux in Lungs. A Pitfall for Pharmacological Studies of Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 Feb;62(2):178-190. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0147OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31419911 Free PMC article.
-
Current advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: the pathogenesis, therapeutic strategies and candidate molecules.Future Med Chem. 2019 Oct;11(19):2595-2620. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2019-0111. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31633402 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxymatrine inhibits TGF‑β1‑mediated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling in alveolar epithelial cells via activation of PI3K/AKT signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Mar 20;25(5):198. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11897. eCollection 2023 May. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37090069 Free PMC article.
-
Shotgun Lipidomics Revealed Altered Profiles of Serum Lipids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Closely Associated with Disease Activity.Biomolecules. 2018 Oct 3;8(4):105. doi: 10.3390/biom8040105. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30282943 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Lipid Metabolism Caused by Inflammation in Cardiac Tissue in the Early Stage of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Murine Model.Metabolites. 2022 May 5;12(5):415. doi: 10.3390/metabo12050415. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35629919 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Hepatic Lipidome Occur in a Gouty Model: A Shotgun Lipidomics Study.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 29;17:7913-7927. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S485979. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39494212 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Steatosis Accompanies Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017 Oct;57(4):448-458. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0242OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28489415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper JA, Jr, White DA, Matthay RA. Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Part 1: cytotoxic drugs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133:321–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

