Wnt signaling pathway participates in valproic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells
- PMID: 25755748
- PMCID: PMC4348902
Wnt signaling pathway participates in valproic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells
Abstract
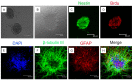
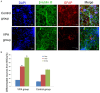
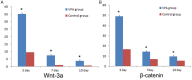
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are multipotent cells that have the capacity for differentiation into the major cell types of the nervous system, i.e. neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed drug for seizures and bipolar disorder in clinic. Previously, a number of researches have been shown that VPA has differential effects on growth, proliferation and differentiation in many types of cells. However, whether VPA can induce NSCs from embryonic cerebral cortex differentiate into neurons and its possible molecular mechanism is also not clear. Wnt signaling is implicated in the control of cell growth and differentiation during CNS development in animal model, but its action at the cellular level has been poorly understood. In this experiment, we examined neuronal differentiation of NSCs induced by VPA culture media using vitro immunochemistry assay. The neuronal differentiation of NSCs was examined after treated with 0.75 mM VPA for three, seven and ten days. RT-PCR assay was employed to examine the level of Wnt-3α and β-catenin. The results indicated that there were more β-tublin III positive cells in NSCs treated with VPA medium compared to the control group. The expression of Wnt-3α and β-catenin in NSCs treated with VPA medium was significantly greater compared to that of control media. In conclusion, these findings indicated that VPA could induce neuronal differentiation of NSCs by activating Wnt signal pathway.
Keywords: Wnt-3α; differentiation; neural stem cells; valproic acid; β-catenin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
c-Jun Amino-Terminal Kinase is Involved in Valproic Acid-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic NSCs and Neurite Outgrowth of NSC-Derived Neurons.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):1254-1266. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2167-7. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28321599 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro characteristics of valproic acid and all-trans-retinoic acid and their combined use in promoting neuronal differentiation while suppressing astrocytic differentiation in neural stem cells.Brain Res. 2015 Jan 30;1596:31-47. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.029. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25463022
-
Valproic acid promotes the neuronal differentiation of spiral ganglion neural stem cells with robust axonal growth.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2728-2735. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30119886
-
[Comprehensive regulation effect of traditional Chinese medicine on proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Nov;42(21):4093-4103. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170928.005. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29271145 Review. Chinese.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Neural Stem Cell Homeostasis and Neurological Diseases.Neuroscientist. 2021 Feb;27(1):58-72. doi: 10.1177/1073858420914509. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Neuroscientist. 2021. PMID: 32242761 Review.
Cited by
-
Lithium chloride promotes proliferation of neural stem cells in vitro, possibly by triggering the Wnt signaling pathway.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2018 Nov 30;23(1):32-41. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2018.1487334. eCollection 2019 Feb. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 30834157 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics and structure-based virtual screening and identification of natural compounds as Wnt signaling modulators: possible therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Divers. 2022 Oct;26(5):2793-2811. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10395-8. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Mol Divers. 2022. PMID: 35146638 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of siRNA targeting of β-catenin on differentiation of rat neural stem cells and gene expression of Ngn1 and BMP4 following in vitro hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3595-601. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5667. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27573468 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun Amino-Terminal Kinase is Involved in Valproic Acid-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic NSCs and Neurite Outgrowth of NSC-Derived Neurons.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):1254-1266. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2167-7. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28321599 Free PMC article.
-
Infusion of Valproic Acid Into the Renal Medulla Activates Stem Cell Population and Attenuates Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Dahl S Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3):1264-1273. doi: 10.1159/000478955. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28693025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goh EL, Ma D, Ming GL, Song H. Adult neural stem cells and repair of the adult central nervous system. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003;12:671–679. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Temple S. Stem cells in the developing and adult nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1998;36:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287:1433–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
