System-wide Analysis of SUMOylation Dynamics in Response to Replication Stress Reveals Novel Small Ubiquitin-like Modified Target Proteins and Acceptor Lysines Relevant for Genome Stability
- PMID: 25755297
- PMCID: PMC4424410
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.O114.044792
System-wide Analysis of SUMOylation Dynamics in Response to Replication Stress Reveals Novel Small Ubiquitin-like Modified Target Proteins and Acceptor Lysines Relevant for Genome Stability
Abstract
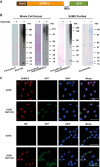
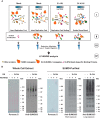
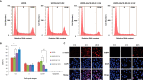
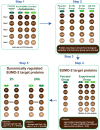
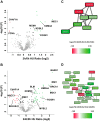
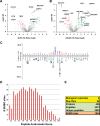
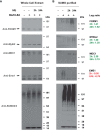
Genotoxic agents can cause replication fork stalling in dividing cells because of DNA lesions, eventually leading to replication fork collapse when the damage is not repaired. Small Ubiquitin-like Modifiers (SUMOs) are known to counteract replication stress, nevertheless, only a small number of relevant SUMO target proteins are known. To address this, we have purified and identified SUMO-2 target proteins regulated by replication stress in human cells. The developed methodology enabled single step purification of His10-SUMO-2 conjugates under denaturing conditions with high yield and high purity. Following statistical analysis on five biological replicates, a total of 566 SUMO-2 targets were identified. After 2 h of hydroxyurea treatment, 10 proteins were up-regulated for SUMOylation and two proteins were down-regulated for SUMOylation, whereas after 24 h, 35 proteins were up-regulated for SUMOylation, and 13 proteins were down-regulated for SUMOylation. A site-specific approach was used to map over 1000 SUMO-2 acceptor lysines in target proteins. The methodology is generic and is widely applicable in the ubiquitin field. A large subset of these identified proteins function in one network that consists of interacting replication factors, transcriptional regulators, DNA damage response factors including MDC1, ATR-interacting protein ATRIP, the Bloom syndrome protein and the BLM-binding partner RMI1, the crossover junction endonuclease EME1, BRCA1, and CHAF1A. Furthermore, centromeric proteins and signal transducers were dynamically regulated by SUMOylation upon replication stress. Our results uncover a comprehensive network of SUMO target proteins dealing with replication damage and provide a framework for detailed understanding of the role of SUMOylation to counteract replication stress. Ultimately, our study reveals how a post-translational modification is able to orchestrate a large variety of different proteins to integrate different nuclear processes with the aim of dealing with the induced DNA damage.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin-SUMO circuitry controls activated fanconi anemia ID complex dosage in response to DNA damage.Mol Cell. 2015 Jan 8;57(1):150-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.001. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25557546 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics Reveals Global Regulation of Protein SUMOylation by ATM and ATR Kinases during Replication Stress.Cell Rep. 2017 Oct 10;21(2):546-558. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.059. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29020638
-
Rap80 protein recruitment to DNA double-strand breaks requires binding to both small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) and ubiquitin conjugates.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25510-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.374116. Epub 2012 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22689573 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted roles of SUMO in DNA metabolism.Nucleus. 2024 Dec;15(1):2398450. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2398450. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Nucleus. 2024. PMID: 39287196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Ubiquitination and SUMOylation in DNA Damage Response.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2020;35:59-84. doi: 10.21775/cimb.035.059. Epub 2019 Aug 18. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31422933 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive compilation of SUMO proteomics.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;17(9):581-95. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.81. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27435506
-
RNF4 Regulates the BLM Helicase in Recovery From Replication Fork Collapse.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 12;12:753535. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.753535. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34868226 Free PMC article.
-
A field guide to the proteomics of post-translational modifications in DNA repair.Proteomics. 2022 Aug;22(15-16):e2200064. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202200064. Epub 2022 Jun 26. Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35695711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preserving genome integrity: The vital role of SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligases.Cell Insight. 2023 Oct 23;2(6):100128. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100128. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cell Insight. 2023. PMID: 38047137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin-specific protease USP36 SUMOylates EXOSC10 and promotes the nucleolar RNA exosome function in rRNA processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 8;51(8):3934-3949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad140. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36912080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deribe Y. L., Pawson T., Dikic I. (2010) Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 666–672 - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C., Mann M. (2010) Decoding signalling networks by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 427–439 - PubMed
-
- Komander D., Rape M. (2012) The Ubiquitin Code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 203–229 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

