Synergy of Histone-Deacetylase Inhibitor AR-42 with Cisplatin in Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 25748177
- PMCID: PMC6371809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.02.2918
Synergy of Histone-Deacetylase Inhibitor AR-42 with Cisplatin in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Cisplatin based chemotherapy regimens form the basis of systemic bladder cancer treatment, although they show limited response rates and efficacy. Recent molecular analysis of bladder cancer revealed a high incidence of mutations in chromatin regulatory genes, suggesting a therapeutic avenue for histone deacetylase inhibitors. We investigated the ability of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor AR-42 to synergize with cisplatin in preclinical models of bladder cancer.
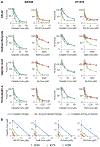
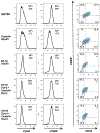
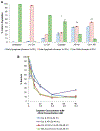
Materials and methods: We assessed the ability of the pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor AR-42 with and without cisplatin to destroy bladder cancer cells by survival and apoptosis assays in vitro, and by growth and differentiation in an in vivo xenograft model. We also assessed the response to the bladder cancer stem cell population by examining the effect of AR-42 on the CD44(+)CD49f(+) population with and without cisplatin. Synergy was calculated using combination indexes.
Results: The AR-42 and cisplatin combination synergistically destroyed bladder cancer cells via apoptosis and it influenced tumor growth and differentiation in vivo. When tested in the CD44(+)CD49f(+) bladder cancer stem cell population, AR-42 showed greater efficacy with and without cisplatin.
Conclusions: AR-42 may be an attractive novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with activity against bladder cancer. Its efficacy in bladder cancer stem cells and synergy with cisplatin warrant further clinical investigation. Our in vitro and animal model studies provide preclinical evidence that AR-42 may be administered in conjunction with cisplatin based chemotherapy to improve the treatment of bladder cancer in patients.
Keywords: apoptosis; chromatin; cisplatin; histone deacetylase inhibitors; urinary bladder neoplasms.
Copyright © 2015 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effect of a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (AR-42) on Canine Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastasis.Prostate. 2017 May;77(7):776-793. doi: 10.1002/pros.23318. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Prostate. 2017. PMID: 28181686
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A synergistically resensitizes a cisplatin resistant human bladder cancer cell line.J Urol. 2011 Mar;185(3):1102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.10.034. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 21255805
-
AR-42 induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via HDAC5 inhibition.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22285-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8077. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26993777 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Histone Deacetylases in Human Tumorigenesis: The Paradigm of Urothelial Bladder Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 14;20(6):1291. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061291. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30875794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of histone deacetylase inhibitors for bladder cancer treatment.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Jun;11(6):959-65. doi: 10.1586/era.10.230. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21707293 Review.
Cited by
-
A phase 1 trial of the HDAC inhibitor AR-42 in patients with multiple myeloma and T- and B-cell lymphomas.Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 Oct;58(10):2310-2318. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1298751. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017. PMID: 28270022 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor AR-42 inhibits breast cancer cell growth and demonstrates a synergistic effect in combination with 5-FU.Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):1967-1974. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8854. Epub 2018 May 31. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008890 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Wheat Germ Protein with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor AR42 Demonstrates Enhanced Cytotoxicity against Lymphoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7866. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147866. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063110 Free PMC article.
-
AR-42: A Pan-HDAC Inhibitor with Antitumor and Antiangiogenic Activities in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Dec 19;13:4321-4330. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S211665. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31908417 Free PMC article.
-
Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces synergistic cytotoxicity with chemotherapy via suppression of Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in urothelial carcinoma.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Dec;96(12):1307-1318. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1697-7. Epub 2018 Oct 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30288546
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11. - PubMed
-
- Von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT et al.: Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 3068. - PubMed
-
- Drayton RM and Catto JWF: Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2012; 12: 271. - PubMed
-
- Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T et al.: HDAC family: what are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett 2009; 277: 8. - PubMed
-
- Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanisms and clinical significance in cancer: HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008; 615: 261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

