Cardiac tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 4 dictates cardiomyocyte contractility and differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes: Road to therapy
- PMID: 25745981
- PMCID: PMC4417452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.01.091
Cardiac tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease 4 dictates cardiomyocyte contractility and differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes: Road to therapy
Abstract
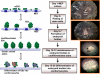
Background: TIMP4 (Tissue Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloprotease 4), goes down in failing hearts and mice lacking TIMP4 show poor regeneration capacity after myocardial infarction (MI). This study is based on our previous observation that administration of cardiac inhibitor of metalloproteinase (~TIMP4) attenuates oxidative stress and remodeling in failing hearts. Therefore, we hypothesize that TIMP4 helps in cardiac regeneration by augmenting contractility and inducing the differentiation of cardiac progenitor cells into cardiomyocytes.
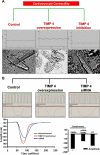
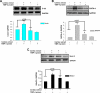
Methods: To validate this hypothesis, we transfected mouse cardiomyocytes with TIMP4 and TIMP4-siRNA and performed contractility studies in the TIMP4 transfected cardiomyocytes as compared to siRNA-TIMP4 transfected cardiomyocytes. We evaluated the calcium channel gene serca2a (sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase2a) and mir122a which tightly regulates serca2a to explain the changes in contractility. We treated mouse embryonic stem cells with cardiac extract and cardiac extract minus TIMP4 (using TIMP4 monoclonal antibody) to examine the effect of TIMP4 on differentiation of cardiac progenitor cells.
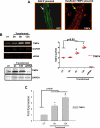
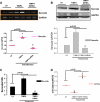
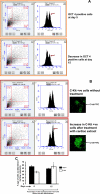
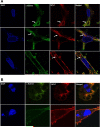
Results: Contractility was augmented in the TIMP4 transfected cardiomyocytes as compared to siRNA-TIMP4 transfected cardiomyocytes. There was elevated expression of serca2a in the TIMP4 transformed myocytes and down regulation of mir122a. The cells treated with cardiac extract containing TIMP4 showed cardiac phenotype in terms of Ckit+, GATA4+ and Nkx2.5 expression.
Conclusion: This is a novel report suggesting that TIMP4 augments contractility and induces differentiation of progenitor cells into cardiac phenotype. In view of the failure of MMP9 inhibitors for cardiac therapy, TIMP4 provides an alternative approach, being an indigenous molecule and a natural inhibitor of MMP9.
Keywords: Cardiomyocytes; Contractility; MicroRNA; Stem cells; Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease (TIMP).
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of TIMP4 in heart failure.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Nov;20(11):2089-2101. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12901. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27396717 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-146b-5p promotes atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation by repressing TIMP4.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10543-10553. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16985. Epub 2021 Oct 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34643044 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial recovery from ischemia-reperfusion is compromised in the absence of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 4.Circ Heart Fail. 2014 Jul;7(4):652-62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001113. Epub 2014 May 19. Circ Heart Fail. 2014. PMID: 24842912
-
Cardiac matrix: a clue for future therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24055000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Embryonic stem cell transplantation: promise and progress in the treatment of heart disease.BioDrugs. 2008;22(6):361-74. doi: 10.2165/0063030-200822060-00003. BioDrugs. 2008. PMID: 18998754 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial pathways to cardiac recovery: TFAM.Heart Fail Rev. 2016 Sep;21(5):499-517. doi: 10.1007/s10741-016-9561-8. Heart Fail Rev. 2016. PMID: 27166683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior mechanical recovery in male and female MRL/MpJ tendons is associated with a unique genetic profile.J Orthop Res. 2021 Jun;39(6):1344-1354. doi: 10.1002/jor.24705. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Orthop Res. 2021. PMID: 32352601 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-4 deletion in mice impacts maternal cardiac function during pregnancy and postpartum.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023 Jan 1;324(1):H85-H99. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00408.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36459450 Free PMC article.
-
The TIMP protein family: diverse roles in pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):C917-C934. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00699.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38284123 Review.
-
Epigenetic silencing of TIMP4 in heart failure.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Nov;20(11):2089-2101. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12901. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27396717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li YY, McTiernan CF, Feldman AM. Interplay of matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases and their regulators in cardiac matrix remodeling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000;46:214–224. - PubMed
-
- Spinale FG. Myocardial matrix remodeling and the matrix metalloproteinases: influence on cardiac form and function. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:1285–1342. - PubMed
-
- Heymans S, Luttun A, Nuyens D, Theilmeier G, Creemers E, Moons L, et al. Inhibition of plasminogen activators or matrix metalloproteinases prevents cardiac rupture but impairs therapeutic angiogenesis and causes cardiac failure. Nat. Med. 1999;5:1135–1142. - PubMed
-
- Lindsey ML, Escobar GP, Mukherjee R, Goshorn DK, Sheats NJ, Bruce JA, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 affects connexin-43 levels, electrical conduction, and survival after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2006;113:2919–2928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

