Mechanisms of growth inhibition of Phytomonas serpens by the alkaloids tomatine and tomatidine
- PMID: 25742263
- PMCID: PMC4371217
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760140097
Mechanisms of growth inhibition of Phytomonas serpens by the alkaloids tomatine and tomatidine
Abstract
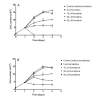
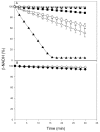
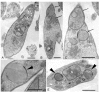
Phytomonas serpens are flagellates in the family Trypanosomatidae that parasitise the tomato plant (Solanum lycopersicum L.), which results in fruits with low commercial value. The tomato glycoalkaloid tomatine and its aglycone tomatidine inhibit the growth of P. serpens in axenic cultures. Tomatine, like many other saponins, induces permeabilisation of the cell membrane and a loss of cell content, including the cytosolic enzyme pyruvate kinase. In contrast, tomatidine does not cause permeabilisation of membranes, but instead provokes morphological changes, including vacuolisation. Phytomonas treated with tomatidine show an increased accumulation of labelled neutral lipids (BODYPY-palmitic), a notable decrease in the amount of C24-alkylated sterols and an increase in zymosterol content. These results are consistent with the inhibition of 24-sterol methyltransferase (SMT), which is an important enzyme that is responsible for the methylation of sterols at the 24 position. We propose that the main target of tomatidine is the sterols biosynthetic pathway, specifically, inhibition of the 24-SMT. Altogether, the results obtained in the present paper suggest a more general effect of alkaloids in trypanosomatids, which opens potential therapeutic possibilities for the treatment of the diseases caused by these pathogens.
Figures
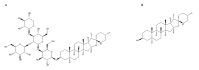
Similar articles
-
Tomatidine promotes the inhibition of 24-alkylated sterol biosynthesis and mitochondrial dysfunction in Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes.Parasitology. 2012 Sep;139(10):1253-65. doi: 10.1017/S0031182012000522. Epub 2012 May 1. Parasitology. 2012. PMID: 22716777
-
Dual effects of plant steroidal alkaloids on Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Aug;50(8):2732-40. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00289-06. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16870766 Free PMC article.
-
Antiprotozoal Effects of the Tomato Tetrasaccharide Glycoalkaloid Tomatine and the Aglycone Tomatidine on Mucosal Trichomonads.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Nov 23;64(46):8806-8810. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04030. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27934291
-
The steroidal alkaloids α-tomatine and tomatidine: Panorama of their mode of action and pharmacological properties.Steroids. 2021 Dec;176:108933. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2021.108933. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Steroids. 2021. PMID: 34695457 Review.
-
Chemistry and anticarcinogenic mechanisms of glycoalkaloids produced by eggplants, potatoes, and tomatoes.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Apr 8;63(13):3323-37. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00818. Epub 2015 Mar 30. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25821990 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Therapeutic Effects of Natural Compounds Against Saprolegnia spp. (Oomycota) and Amyloodinium ocellatum (Dinophyceae).Front Vet Sci. 2020 Feb 21;7:83. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00083. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32154278 Free PMC article.
-
Not in your usual Top 10: protists that infect plants and algae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Apr;19(4):1029-1044. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12580. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29024322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Not all saponins have a greater antiprotozoal activity than their related sapogenins.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019 Jul 1;366(13):fnz144. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz144. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31271417 Free PMC article.
-
Combination With Tomatidine Improves the Potency of Posaconazole Against Trypanosoma cruzi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Mar 4;11:617917. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.617917. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33747979 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Artemisia pedemontana subsp. assoana Essential Oils and Hydrolate.Biomolecules. 2019 Oct 2;9(10):558. doi: 10.3390/biom9100558. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31581691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beach DH, Goad LJ, Holz GG. Effects of ketoconazole in sterol biosynthesis byTrypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986;136:851–856. - PubMed
-
- Beveridge THJ, Li TSC, Drover Phytosterol content in American ginseng seed oil. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50:744–750. - PubMed
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Burbiel J, Bracher F. Azasteroids as antifungals. Steroids. 2003;68:587–594. - PubMed
-
- Camargo EP, Kastelein P, Roitman I. Trypanosomatid parasites of plants (Phytomonas) Parasitol Today. 1990;6:22–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

