Death Receptor-Mediated Cell Death and Proinflammatory Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- PMID: 25729762
- PMCID: PMC4340657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.11.005
Death Receptor-Mediated Cell Death and Proinflammatory Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
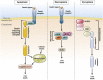
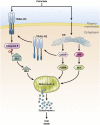
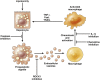
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming public health problem worldwide. A subset of patients develop an inflammatory disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by steatosis, hepatocellular death, macrophage and neutrophil accumulation and varying stages of fibrosis. Hepatocyte cell death triggers the cellular inflammatory response and, therefore, reducing cell death may be salutary in the steatohepatitis disease process. Recently, a better understanding of hepatocyte apoptosis in NASH has been obtained and new information regarding other cell death modes, such as necroptosis and pyroptosis, has been reported. Hepatocyte lipotoxicity is often triggered by death receptors. In addition to causing apoptosis, death receptors have been shown to mediate proinflammatory signaling, suggesting that apoptosis in this context is not an immunologically silent process. Here we review recent developments in our understanding of hepatocyte cell death by death receptors and its mechanistic link to inflammation in NASH. We emphasize how proapoptotic signaling by death receptors may induce the release of proinflammatory extracellular vesicles, thereby recruiting and activating macrophages and promoting the steatohepatitis process. Potential therapeutic strategies are discussed based on this evolving information.
Keywords: apoptosis; caspase inhibitor; cell death; death receptors; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; fibrosis; inflammasome; inflammation; microvesicles; necroptosis; pyroptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview.Hepatol Commun. 2020 Jan 14;4(4):478-492. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1479. eCollection 2020 Apr. Hepatol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32258944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte apoptosis, expression of death receptors, and activation of NF-kappaB in the liver of nonalcoholic and alcoholic steatohepatitis patients.Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Sep;99(9):1708-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.40009.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15330907
-
Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 14;20(42):15539-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15539. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25400438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progression of non-alcoholic steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis parallels cumulative accumulation of danger signals that promote inflammation and liver tumors in a high fat-cholesterol-sugar diet model in mice.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 16;13:193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0552-7. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26077675 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-caspase inhibitor VX-166 reduces fibrosis in an animal model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Hepatology. 2009 Nov;50(5):1421-30. doi: 10.1002/hep.23167. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19676126
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus plantarum C88 protects against aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury in mice via inhibition of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses and excessive apoptosis.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Jul 29;19(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1525-4. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31357935 Free PMC article.
-
Excessive gluconeogenesis causes the hepatic insulin resistance paradox and its sequelae.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 15;8(12):e12294. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12294. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36582692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH).Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 13;7(1):287. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01119-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35963848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Customized liver organoids as an advanced in vitro modeling and drug discovery platform for non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jul 9;19(11):3595-3613. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.85145. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37497008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Promoting Kinases.Semin Liver Dis. 2020 Nov;40(4):346-357. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713115. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Semin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 32526787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fujii H., Kawada N. Inflammation and fibrogenesis in steatohepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:215–225. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
