The effects of knockdown of rho-associated kinase 1 and zipper-interacting protein kinase on gene expression and function in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 25723491
- PMCID: PMC4344299
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116969
The effects of knockdown of rho-associated kinase 1 and zipper-interacting protein kinase on gene expression and function in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells
Abstract
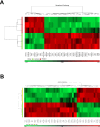
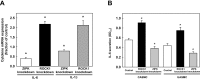
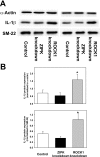
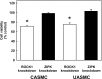
Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and zipper-interacting protein kinase (ZIPK) have been implicated in diverse physiological functions. ROCK1 phosphorylates and activates ZIPK suggesting that at least some of these physiological functions may require both enzymes. To test the hypothesis that sequential activation of ROCK1 and ZIPK is commonly involved in regulatory pathways, we utilized siRNA to knock down ROCK1 and ZIPK in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells (SMC). Microarray analysis using a whole-transcript expression chip identified changes in gene expression induced by ROCK1 and ZIPK knockdown. ROCK1 knockdown affected the expression of 553 genes, while ZIPK knockdown affected the expression of 390 genes. A high incidence of regulation of transcription regulator genes was observed in both knockdowns. Other affected groups included transporters, kinases, peptidases, transmembrane and G protein-coupled receptors, growth factors, phosphatases and ion channels. Only 76 differentially expressed genes were common to ROCK1 and ZIPK knockdown. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified five pathways shared between the two knockdowns. We focused on cytokine signaling pathways since ROCK1 knockdown up-regulated 5 and down-regulated 4 cytokine genes, in contrast to ZIPK knockdown, which affected the expression of only two cytokine genes (both down-regulated). IL-6 gene expression and secretion of IL-6 protein were up-regulated by ROCK1 knockdown, whereas ZIPK knockdown reduced IL-6 mRNA expression and IL-6 protein secretion and increased ROCK1 protein expression, suggesting that ROCK1 may inhibit IL-6 secretion. IL-1β mRNA and protein levels were increased in response to ROCK1 knockdown. Differences in the effects of ROCK1 and ZIPK knockdown on cell cycle regulatory genes suggested that ROCK1 and ZIPK regulate the cell cycle by different mechanisms. ROCK1, but not ZIPK knockdown reduced the viability and inhibited proliferation of vascular SMC. We conclude that ROCK1 and ZIPK have diverse, but predominantly distinct regulatory functions in vascular SMC and that ROCK1-mediated activation of ZIPK is not involved in most of these functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rho-associated kinase and zipper-interacting protein kinase, but not myosin light chain kinase, are involved in the regulation of myosin phosphorylation in serum-stimulated human arterial smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 13;14(12):e0226406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226406. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31834925 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK1 phosphorylates and activates zipper-interacting protein kinase.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):4884-4893. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609990200. Epub 2006 Dec 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17158456
-
The effect of zipper-interacting protein kinase on high glucose-stimulated human aortic smooth muscle cells.Int J Mol Med. 2014 May;33(5):1305-11. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1697. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24626840
-
Zipper interacting protein kinase (ZIPK): function and signaling.Apoptosis. 2014 Feb;19(2):387-91. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0934-3. Apoptosis. 2014. PMID: 24193917 Review.
-
The regulation of smooth muscle contractility by zipper-interacting protein kinase.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;85(1):79-87. doi: 10.1139/y06-103. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17487247 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic Mechanical Stretch Up-regulates Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor Expression in Cultured Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells.Biosci Rep. 2018 Apr 27;38(2):BSR20171398. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171398. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29467272 Free PMC article.
-
A novel inhibitory effect of oxazol-5-one compounds on ROCKII signaling in human coronary artery vascular smooth muscle cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 30;6:32118. doi: 10.1038/srep32118. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27573465 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-associated kinase and zipper-interacting protein kinase, but not myosin light chain kinase, are involved in the regulation of myosin phosphorylation in serum-stimulated human arterial smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 13;14(12):e0226406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226406. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31834925 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic mice overexpressing desmocollin-2 (DSC2) develop cardiomyopathy associated with myocardial inflammation and fibrotic remodeling.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 24;12(3):e0174019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174019. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28339476 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

